Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Alzheimer’s Disease
There is currently no cure for AD. Currently available medications offer relatively small symptomatic benefit for some patients, but do not slow down disease progression. TACRINE : a. Memantine b. Donepezil c. Galantamine or galanthamine d. Rivastigmine
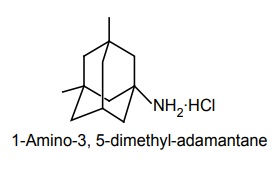
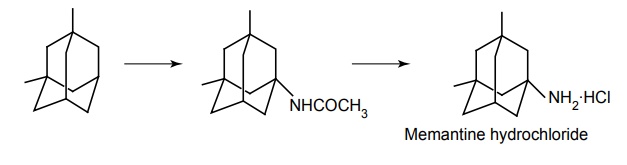
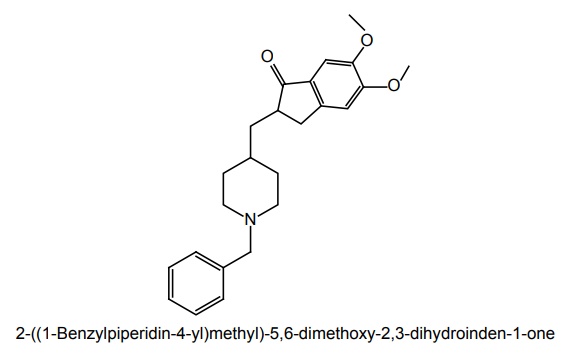
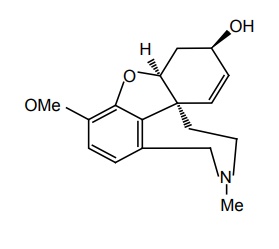
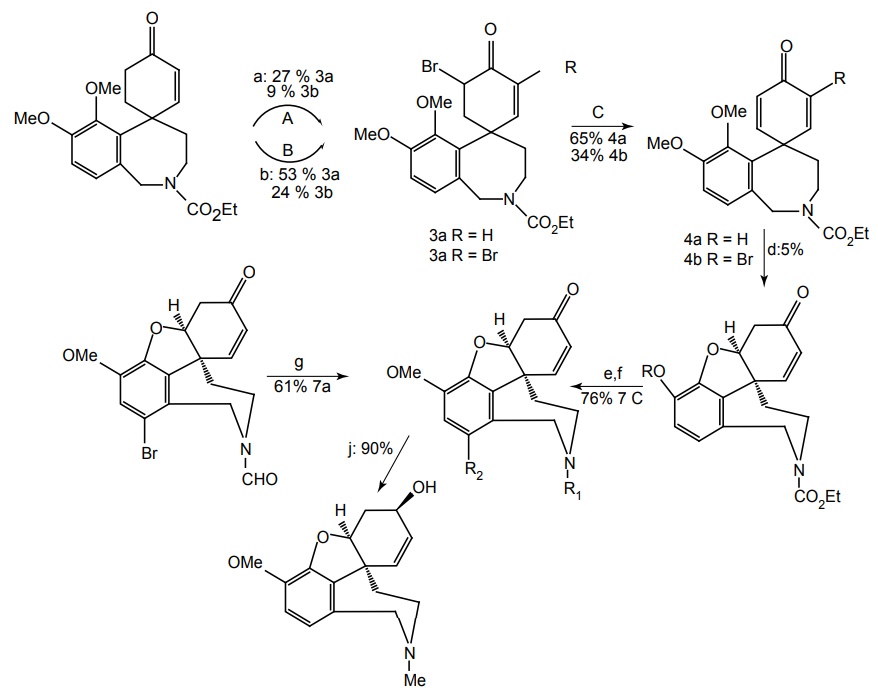
There is currently no cure for AD. Currently available medications offer relatively small symptomatic benefit for some patients, but do not slow down disease progression. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition was thought to be important because there is a reduction in the activity of the cholinergic neurons. AChE-inhibitors reduce the rate at which acetylcholine (ACh) is broken down, and hence, increase in the concentration of ACh in the brain (combating the loss of ACh caused by the death of the cholinergic neurons). Tacrine—no longer clinically used; Donepezil— marketed as Aricept; Galantamine—marketed as Razadyne, Reminyl, or Nivalin; Rivastigmine— marketed as Exelon. Recent evidence of the involvement of glutaminergic neuronal excito-toxicity in the aetiology of AD led to the development and introduction of memantine. Memantine is a novel NMDA receptor antagonist, and has been shown to be moderately clinically efficacious. Properties and its uses: It is a parasympathomimetic and a centrally acting cholinesterase inhibitor (anticholinesterase). It was the first centrally acting cholinesterase inhibitor approved for the treatment of AD, and was marketed under the trade name Cognex. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is the first in a novel class of AD medications acting on the glutaminergic system by blocking NMDA glutamate receptors. Properties and uses: It is marketed under the trade name, Aricept, and is a centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Its main therapeutic use is in the treatment of AD where it is used to increase cortical acetylcholine. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is an alkaloid obtained from the bulbs and flowers of the Caucasian snowdrop (Voronov’s snowdrop), Galanthus woronowii (Amaryllidaceae), and related genera such as Narcissus (daffodil), Leucojum (snowflake), and Lycoris, including Lycoris radiata (red spider lily). It is also synthetically prepared. The active ingredient that was isolated from a species traditonally used as a popular medicine in Eastern Europe. It has been used for decades in Eastern Europe especially in the symptomatic treatment of polio (poliomyelitis) and was later developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals into the Alzheimer medication. Treatment
ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS
NMDA ANTAGONISTS
TACRINE
a. Memantine
b. Donepezil
c. Galantamine or galanthamine
d. Rivastigmine
Related Topics
