Para amino benzoic acid derivatives
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Local Anaesthetics
a. Benzocaine (Americaine) b. Butamben (Butesin) c. Procaine hydrochloride (Navocaine) d. Tetracaine (Anethaine, Pontocaino hydrochloride) e. Butacaine (Butyn sulphate) f. Binoxinate g. Propoxycaine (Blockhain) h. Proparacaine
Para amino benzoic acid derivatives Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, freely soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in water. Structurally, it lacks the terminal diethylamino group usually present in most of the anaesthetics, such as procaine. It is used to get rid of the pain caused by wounds, ulcers, and in mucous surface. It is nonirritant and nontoxic. Assay: Dissolve the substance in a mixture of hydrochloric acid and water, and perform the determination of primary aromatic amino-nitrogen (diazotization method). Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight container and protected from light. Dose: Topical, 1% to 20% in ointment, cream, and aerosol for skin. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a local anaesthetic of relatively low solubility and used in a similar manner to benzocaine. It is more efficacious than its corresponding ethyl ester when applied to intact mucous membranes. Dose: Topical, 1% to 2% in conjunction with other local anaesthetics in creams, ointments, sprays, and suppositories. Synthesis Route I. From: p-Amino benzoic acid Route II. From: 2-Chloro ethyl 4-amino benzoate Route III. From: 2-Chloro ethanol Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, soluble in water and alcohol. It has the advantage of lacking of local irritation, minimal systemic toxicity, longer duration of action, and low cost. It can be effectively used for causing anaesthesia by infiltration, nerve block, epidural block, or spinal anaesthesia. Assay: Dissolve the substance in dilute hydrochloric acid and perform the determination of primary aromatic amino nitrogen (Diazotization method). Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight container, protected from light. Dose: Usual infiltration, 50 ml of a 0.5% solution; usual peripheral nerve block, 25 ml of a 1% or 2% solution; usual epidural, 25 ml of a 1.5% solution. Synthesis Route I. From: 4-Amino benzoic acid Route II. From: 4-Amino benzoic acid Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, slightly hygroscopic in nature, soluble in alcohol, and freely soluble in water. It is an all-purpose local anaesthetic drug used frequently in surface, infiltration block, caudal, and spinal anaesthesia. It is reported to be 10 times more toxic and potent than procaine. Its duration of action is twice than that of procaine. Assay: Dissolve the substance in alcohol and add 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Perform potentiometric titration, using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight container, protected from light. Dose: Usually, subarachnoid 0.5 to 2 ml as a 0.5% solution; topically, 0.1 ml of a 0.5% solution to the conjunctiva. Dosage forms: Tetracaine eye drops B.P. Synthesis Dose: Several instillations of a 2% solution about 3 min apart allows most surgical procedures. Synthesis Synthesis Properties and uses: Its local anaesthetic potency is reported to be 7 or 8 times more than that of procaine. It is a structural isomer of proparacaine, and is less toxic with slightly lower potency than proparacaine. It is mainly used for infiltration and nerve block anaesthesia. Dose: Usually, 2 to 5 ml of 0.5% solution. Synthesis Properties and uses: An effective ester-type surface anaesthetic with potency about equal to that of tetracaine. It is a useful anaesthetic in ophthalmology and induces little or no initial irritation. It is useful for most occular procedures that require topical anaesthesia such as cataract extraction, tonometry, removal of foreign bodies and sutures, gonioscopy, conjunctival scraping for diagnosis and short-operative procedures involving the cornea and conjunctiva.a. Benzocaine (Americaine)
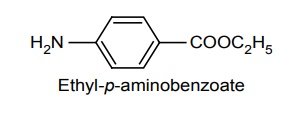
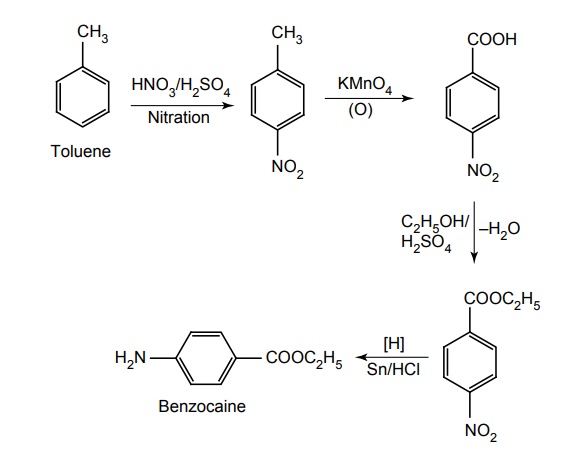
b. Butamben (Butesin)

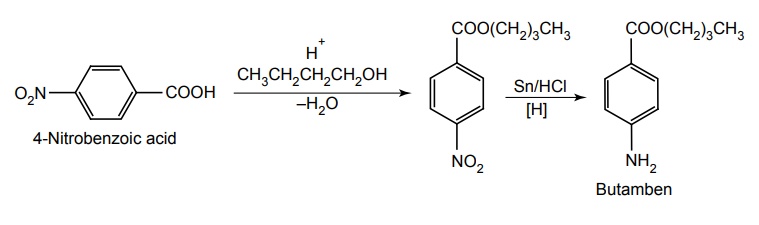
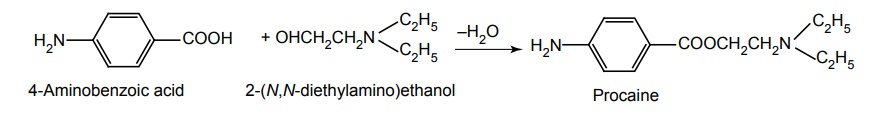
c. Procaine hydrochloride (Navocaine)

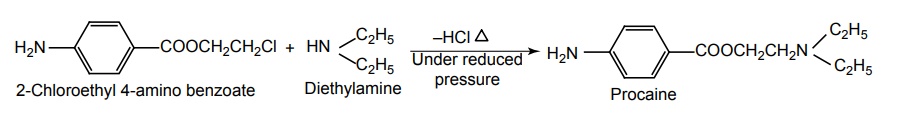
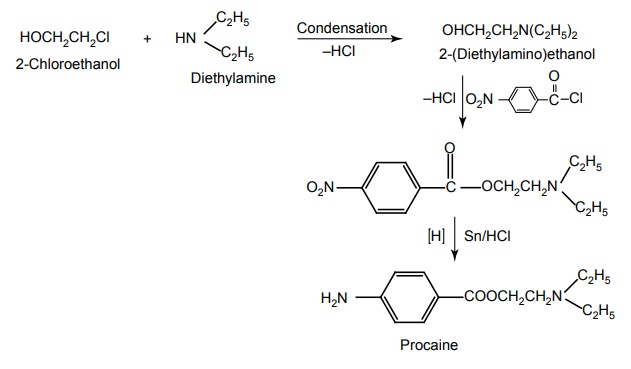
d. Tetracaine (Anethaine, Pontocaino hydrochloride)
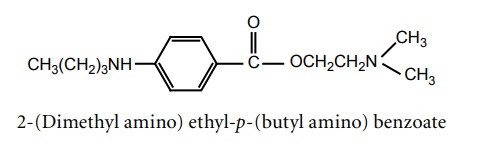

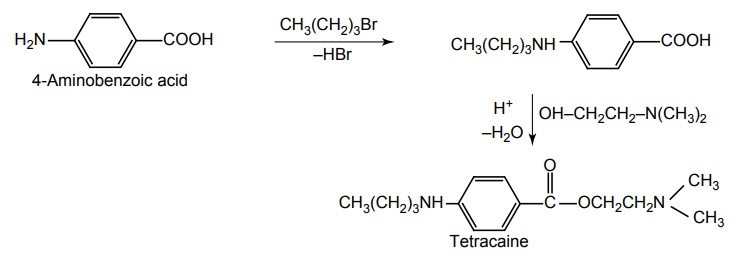
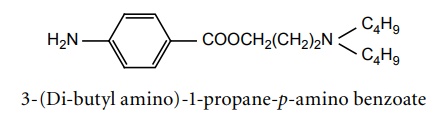
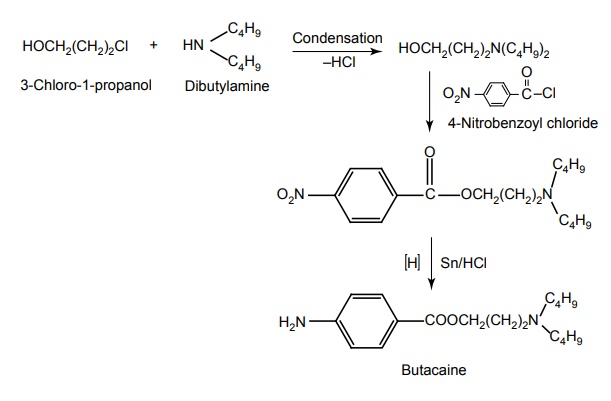
e. Butacaine (Butyn sulphate)
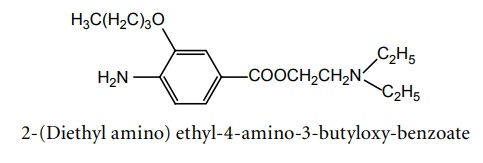
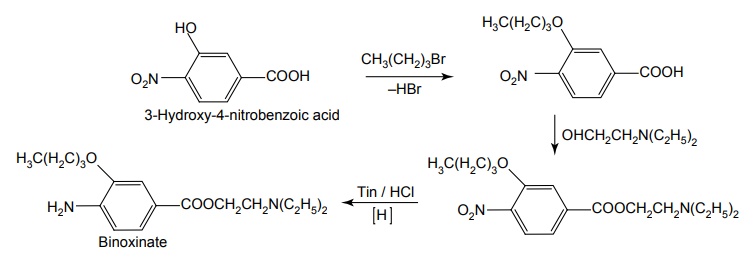
f. Binoxinate
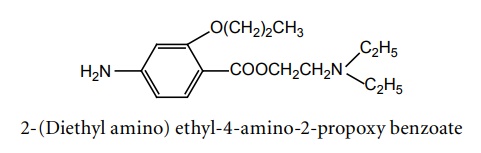
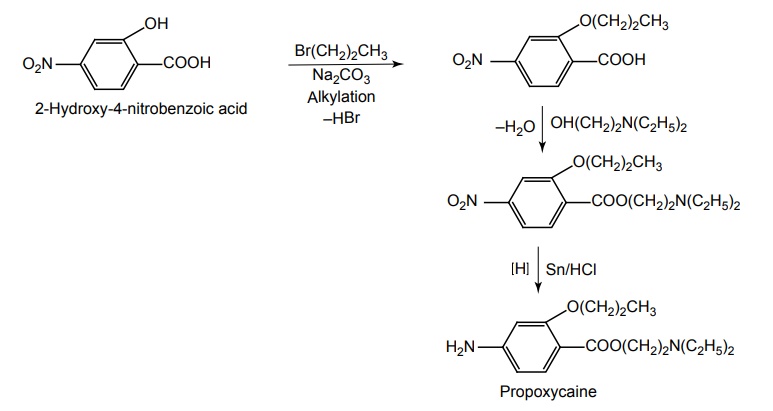
g. Propoxycaine (Blockhain)
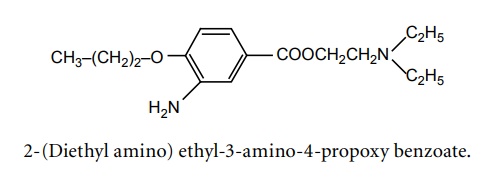
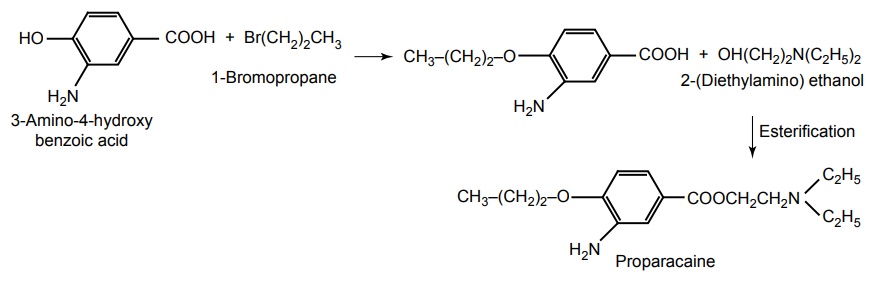
h. Proparacaine
Related Topics
