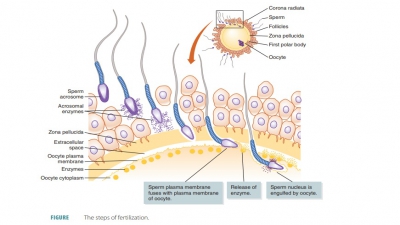
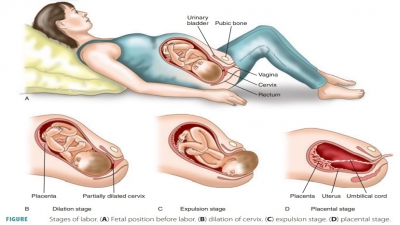
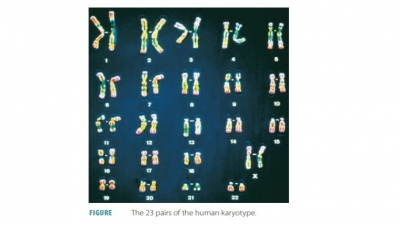
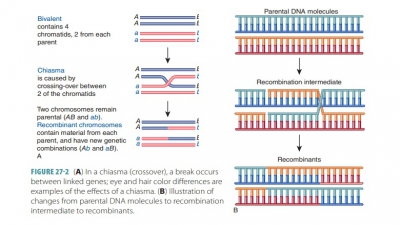
Heredity
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Heredity
The science of genetics is the study of heredity. In the mid-1800s, Gregor Mendel was the first scientist to propose basic principles of heredity.
Heredity
After studying this chapter, the reader should be able to:
1. Identify what was achieved by the Human Genome Project.
2. Define the terms genes,
chromosomes, autosomes, alleles, and homozygous.
3. Distinguish between dominant and recessive alleles.
4. List the three events that occur as part of genetic
variation.
5. Explain the concept of multiple allele inheritance using
the ABO blood group.
6. Identify factors that may influence or override gene
expression.
7. Contrast Prader–Willi syndrome and Angelman’s syndrome.
8. Explain why mitochondrial (extranuclear) genes are usually
transmitted from the mother to her offspring.
9. Identify the newer procedures that will likely replace
amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling.
10. Give
examples of how gene therapy may be used.
Overview
The science of genetics
is the study of heredity. In the
mid-1800s, Gregor Mendel was the first scientist to propose basic principles of
heredity. Today’s genet-icists are
able to engineer and manipulate human genes
in order to examine the ways in which they are expressed. The Human Genome Project was undertaken to
determine the actual human DNA sequence. As the field of genetic screening
develops, many future medical outcomes as yet not even imag-ined will be possible.
Already, the use of the human genome is allowing for drugs to be developed that
are more effective in treating diseases and even curing them.