Fibric acid derivatives
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antihyperlipidaemic Agents
Antihyperlipidaemic Agents : Fibric acid derivatives - Synthesis and Drug Profile- v. Clofibrate vi. Gemfibrosil (Gempar, Lopid, Normolip) vii. Benzafibrate (Beza-Xl, Bezalip) viii. Ciprofibrate ix. Fenofibrate (Lipicard, Stanlip, Fibral)
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Fibric acid derivatives
Mode of action: These drugs activate receptors called α-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, which enhance the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase and increase the degradation of very low-density lipoprotein. This also enhances the fatty acid oxidation.
Metabolism of fibrates: The prodrug fenofibrate undergoes rapid hydrolysis to produce fenofibric acid. This active metabolite can then be further metabolized by oxidative or conjugate pathways.
v. Clofibrate
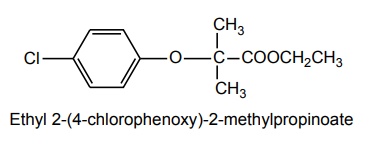
Properties and uses: It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with acid taste, insoluble in water. It is a drug of choice in the treatment of type III, IV, and V hyperlipoproteinaemias.
Synthesis
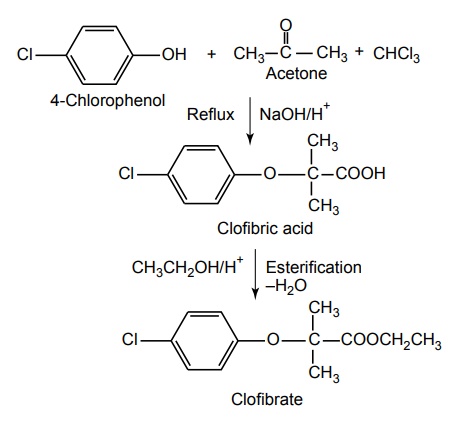
Dosage forms: Clofibrate capsules B.P.
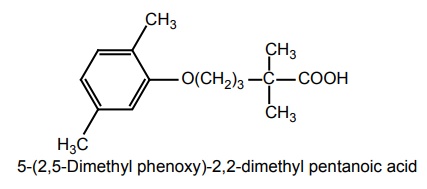
vi. Gemfibrosil (Gempar, Lopid, Normolip)
Metabolism: It is similar to fenofibric acid. It may undergo oxidation or conjugation. Oxidation of aromatic methyl group produces inactive hydroxymethyl and carboxylic acid analogues. As a drug class, fibrate and their oxidized analogues are primarily excreted as glucuronide conjugate in urine. Oxidation requires the CYP3A4 isoenzymes. However, because of the ability of these compounds to be conjugated and eliminated either with or without oxidation, drug interaction with other compounds affecting the CYP3A4 system are less important here than other drug classes.
Properties and uses: It is a white or almost white waxy and crystalline powder, insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride, in ethanol, and in methanol. It was used first in the treatment of hyperlipoprotenemia in the mid-1970s. Its mechanism of action and use are similar to those of clofibrate. It is used in the treatment of hyperlipidaemia. It is also useful in type V hyperlipoproteinaemia.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in methanol, to this add water and 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, and perform potentiometric titration, using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide.
Synthesis
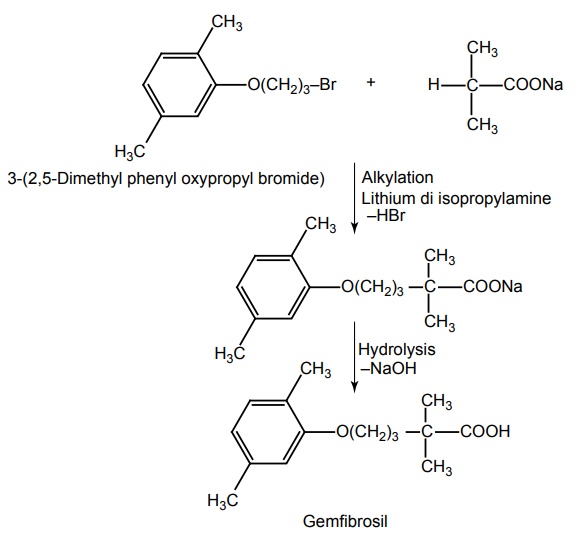
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light. Dose: (Adults only) 600 mg twice daily, taken 30 min before morning and evening meals. Dosage forms: Gemfibrozil capsules B.P., Gemfibrozil tablets B.P.
vii. Benzafibrate (Beza-Xl, Bezalip)
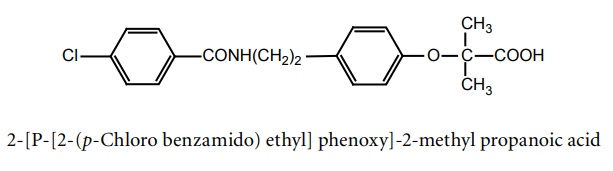
Properties and uses: Benzafibrate is more potent than clofibrate and reduces HDL and LDL to a greater extent. It is a highly potent antihyperlipidaemic agent.
Synthesis
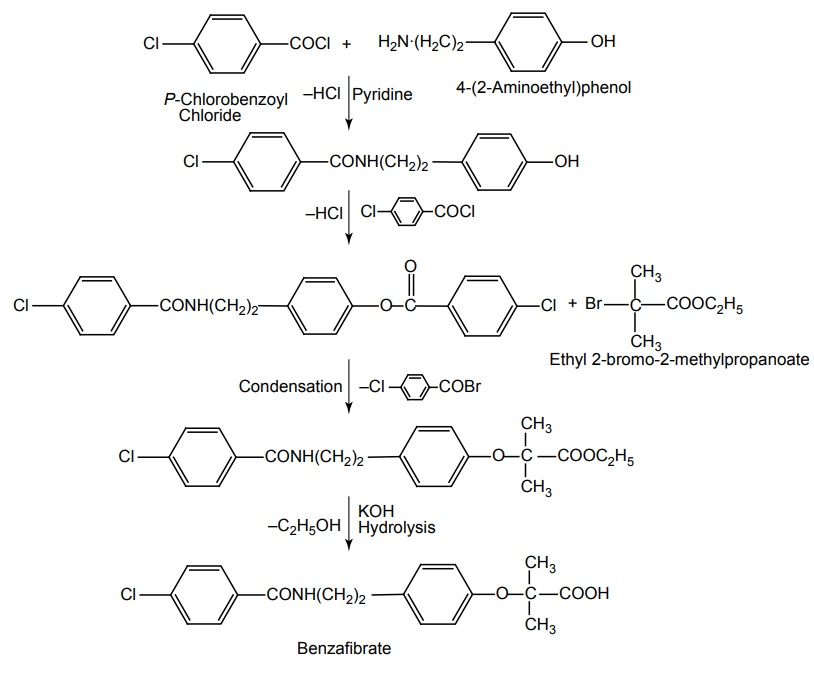
Dose: For hyperlipidaemias: Adult: 200 mg thrice a day, may increase dose gradually over 5–7 days. Maintenance: 200 mg twice a day. As modified-release preparation: 400 mg daily.
viii. Ciprofibrate
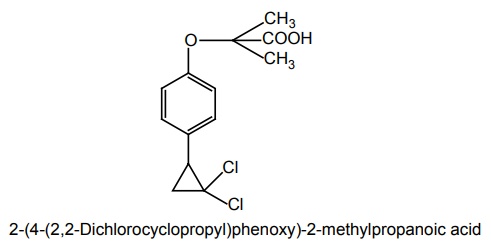
Synthesis
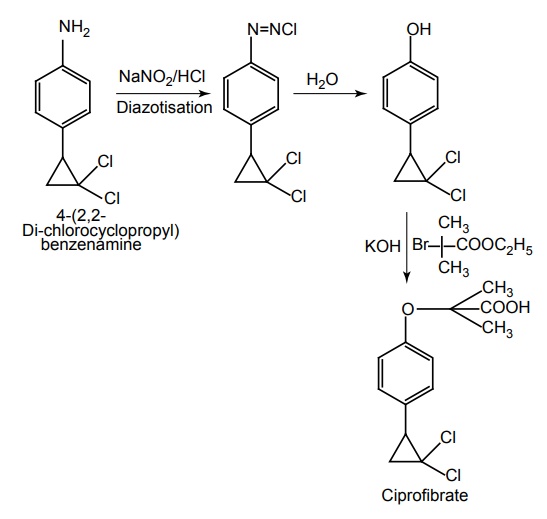
Properties and uses: It is a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder, insoluble in water, soluble in anhydrous ethanol, and in toluene. It is a more potent lipid-lowering agent than clofibrate, used in the treatment of hyperlipidaemic conditions.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of water and anhydrous ethanol. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and determining the end point potentiometrically.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
ix. Fenofibrate (Lipicard, Stanlip, Fibral)
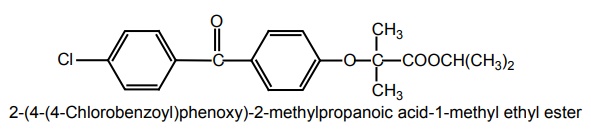
Properties and uses: It is a white or almost white crystalline powder, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in water, and soluble in methylene chloride. Fenofibrate is a more potent hypocholesterolemic and triglycerides lowering agent.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Synthesis
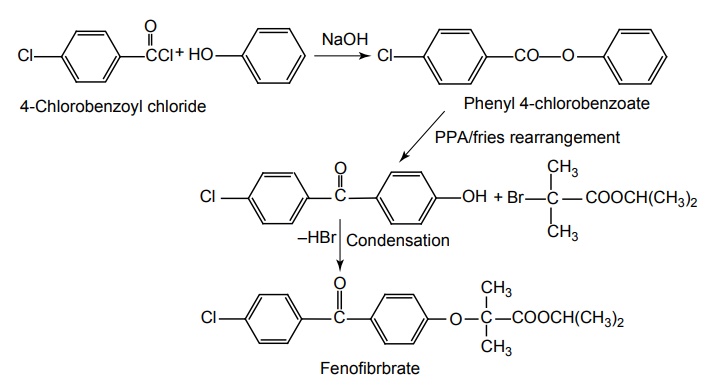
Dose: For hyperlipidaemias: Adult: Dose depends on the formulation used. For standard micronized formulations: Initially, 67 mg thrice a day or 200 mg once daily. For nonmicronized formulations: Initially, 200–300 mg daily in divided doses. Usual range: 200–400 mg daily. For formulations with improved bioavailability, doses between 40 and 160 mg daily may be used. Child: 5 mg/kg daily.
Related Topics
