Alpha-receptor Adrenergic blocking agents
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Adrenergic Blockers
i. Dibenamine ii. Phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline) iii. Tolazoline (Synonym: Priscoline) iv. Phentolamine mesylate v. Prazosin (Minipress, Prazopress) vi. Terazosin (Olyster, Teralfa, Terapress) vii. Doxazosin (Alfazosin, Doxacard, Duracard)
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Alpha-receptor blocking agents
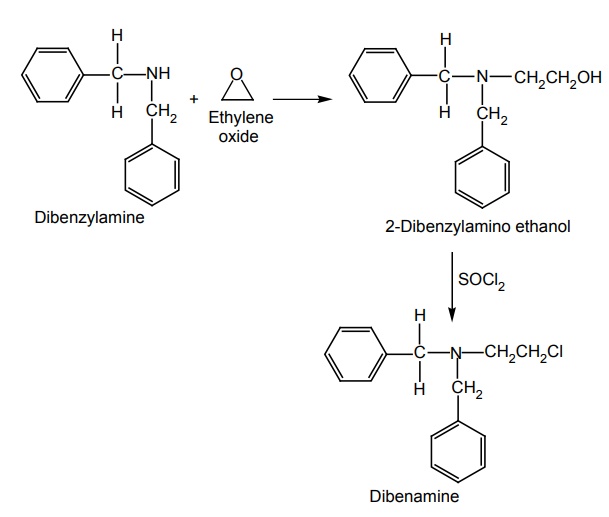
i. Dibenamine
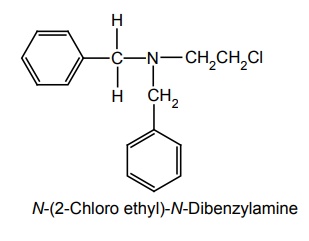
Synthesis
Uses: Used as an antihypertensive agent.
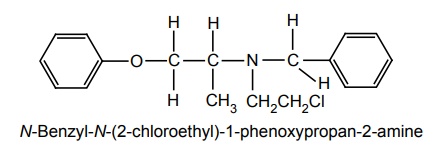
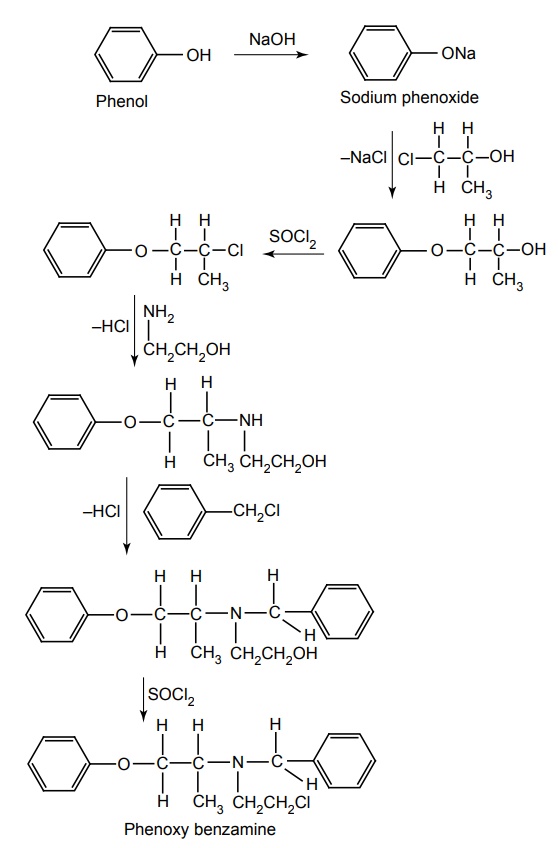
ii. Phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline)
Properties and uses: Colourless, crystalline compound soluble in alcohol, water, and chloroform. Irreversible antagonist with nonselective actions, a major use of phenoxybezamine is in the treatment of pheochromocytoma (tumours of the adrenal medulla). It is used to treat peripheral vascular diseases, such as Raynaud’s syndrome. It has also been used in the case of shock and frostbite to improve blood flow to peripheral tissues. Used in the treatment of shock and in the treatment of pulmonary oedema.
Assay: It is assayed by nonaqueous titration: the solution of the sample is titrated with 0.1 M perchloric acid using oracet blue B as indicator.
Dose: The usual dose initially 10 mg/day, increased gradually to 60 mg/day in divided doses.
Dosage forms: Phenoxybenzamine capsules B.P.
Synthesis
iii. Tolazoline (Synonym: Priscoline)
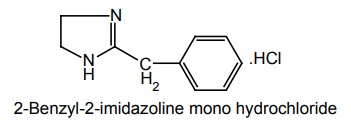
Synthesis
Route I. From: Phenyl acetonitrile
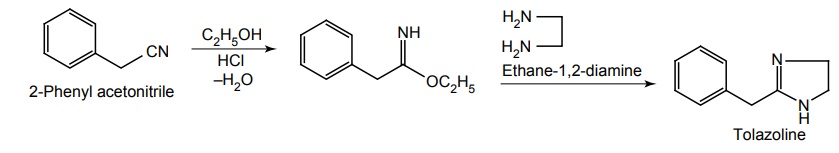
Properties and uses: It is a white, bitter taste, crystalline compound with a slight aromatic odour, soluble in water, alcohol, and chloroform, but sparingly soluble in ether. It is an imidazolidine derivative. It is a competitive alpha adrenergic antagonist and possesses similar affinity for α1 and α2 receptors. It is a vasodilator and has a sympathomimetic effect to stimulate the heart and causes mydriasis. It is of some use in the treatment of Raynaud’s disease, cerebral vascular accidents. It has been used in the treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Dose: By I.M., I.V., S.C., for adults: 25 mg slowly, then increased upto 50 to 75 mg twice/day to 2 or 3 times/week.
iv. Phentolamine mesylate
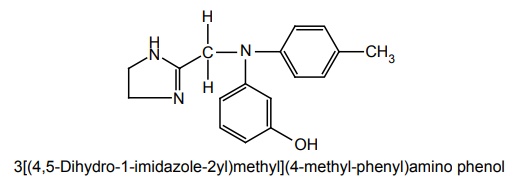
Synthesis
Route I: From 3-(p-Toluidino) phenol
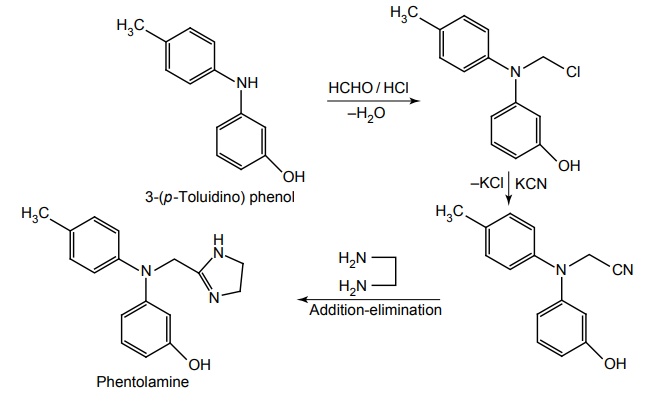
Route II: From 2-chloroacetyl chloride
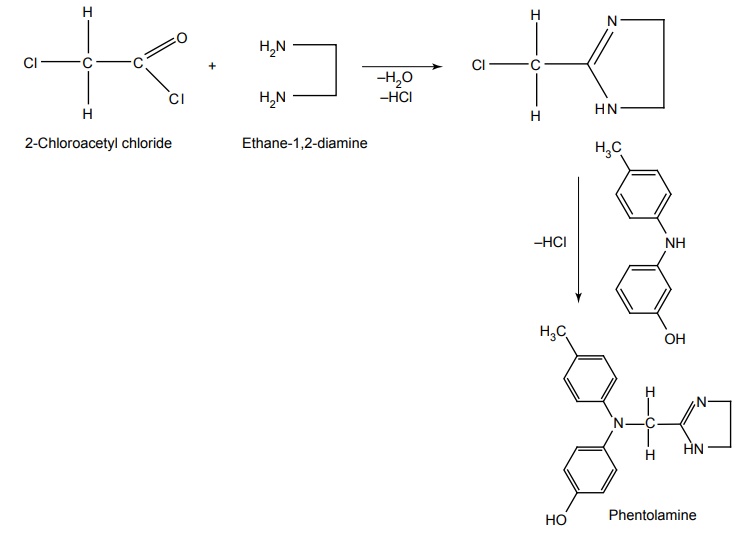
Properties and uses: It is a white, odourless, bitter powder, soluble in water and alcohol. Phentolamine is a nonselective α-adrenoreceptor antagonist with an immediate onset and short duration of action. In addition to α-blocking activity, it has weak muscarnic activity in the gastrointestinal tract and weak to mild histaminergic activity in the stomach. It is an α-adrenergic blocker used in urgent heart failure.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in 2-propanol and titrate under a current of nitrogen with 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in 2-propanol. Determine the end point potentiometrically, using a glass electrode as an indicator electrode and a calomel electrode containing a saturated solution of tetramethylammonium chloride in 2-propanol as the comparison electrode.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dosage forms: Phentolamine mesylate injection I.P., Phentolamine injection B.P.
v. Prazosin (Minipress, Prazopress)
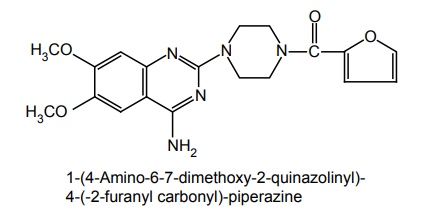
Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, soluble in water and alcohol. A selective α-antagonist, prazosin, reduces peripheral vascular resistance and lowers arterial blood pressure in both supine and erect patients. Dizziness, headache, and palpitations can occur. Used to treat hypertension of any degree. It has been used in decreasing cardiac overload.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in acetic anhydride and add anhydrous formic acid. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid and determine the end point potentiometrically.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dose: For hypertension: the adult dose as hydrochloride: Initially, 500 μg twice to thrice/day for 3–7 days, increased to 1 mg two times to three times for the next 3–7 days if tolerated and gradually increased thereafter according to the patient’s response. Maximum dose is 20 mg/day.
Synthesis
Route I. From: 4, 5-Dimethoxy anthranilamide
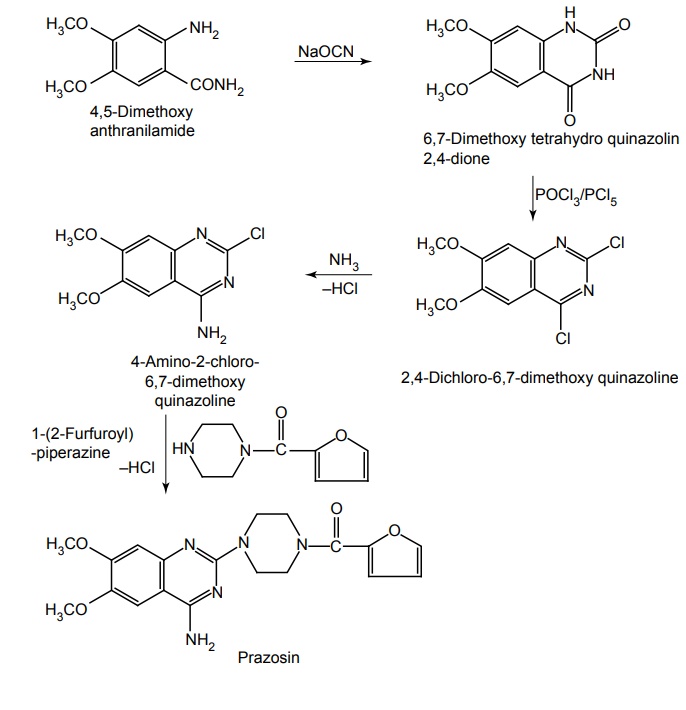
Route II. From: 4,5-Dimethoxy anthranilic acid
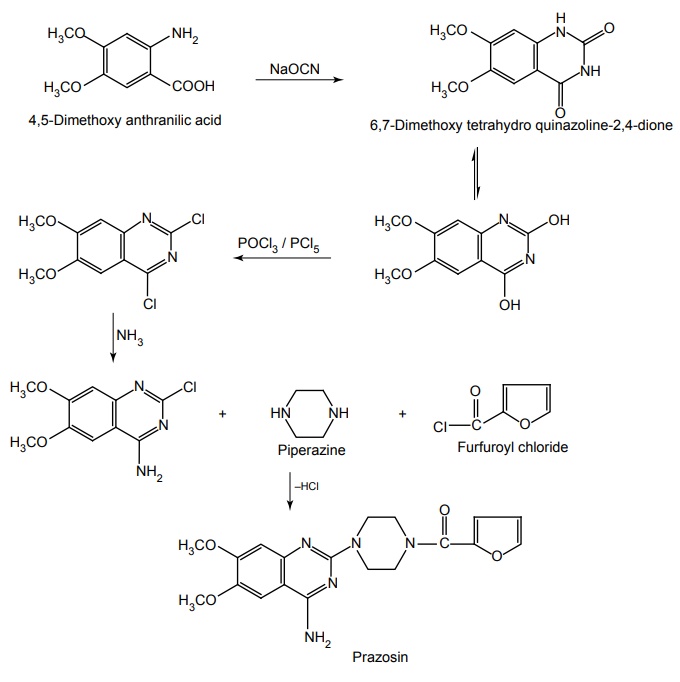
For heart failure: The adult dose as hydrochloride is initially, 500 μg twice to thrice/day, gradually increased according to response, maintenance dose is 4–20 mg day.
For Raynaud’s syndrome: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): The adult dose initially is 500 μg twice/ day, increased to a maintenance dose of <2 mg twice/day.
Dosage forms: Prazosin tablets I.P., B.P.
vi. Terazosin (Olyster, Teralfa, Terapress)

Synthesis
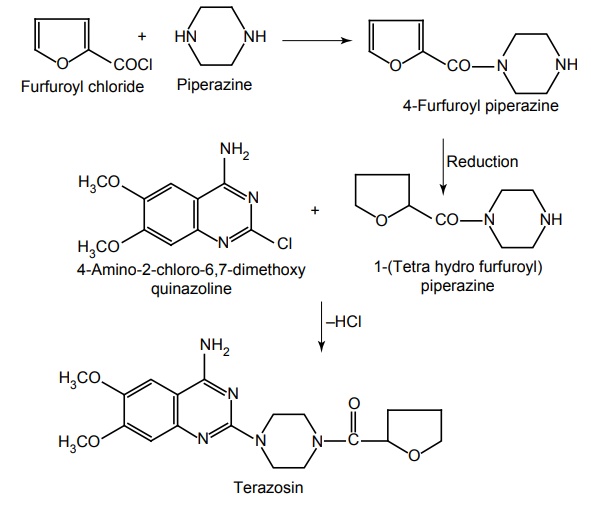
Properties and uses: It is a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder, insoluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol and ethanol. This α1 -adrenergic receptor blocker has a longer half life (12 h) and longer duration of action (24 h) than prazosin, but is otherwise, similar to prazosin. Because the α1 -selective drugs have little action on presynaptic receptors, they do not increase norepinephrine concentrations and reflex sympathetic activity (tachycardia) is less likely to occur.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid methanol. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and determine the end point potentiometrically.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dose: For hypertension: The initial dose for adult is 1 mg at bed time, gradually increased two to three times a day according to the patient’s response. Maintenance dose is 2–10 mg once daily. Maximum effect observed with 20 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses.
vii. Doxazosin (Alfazosin, Doxacard, Duracard)
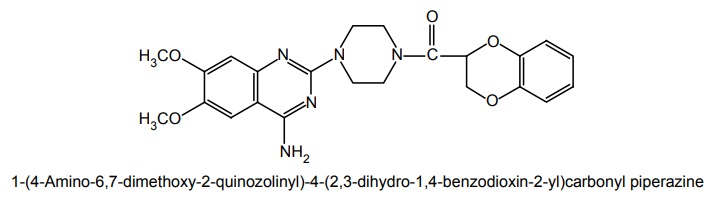
Synthesis
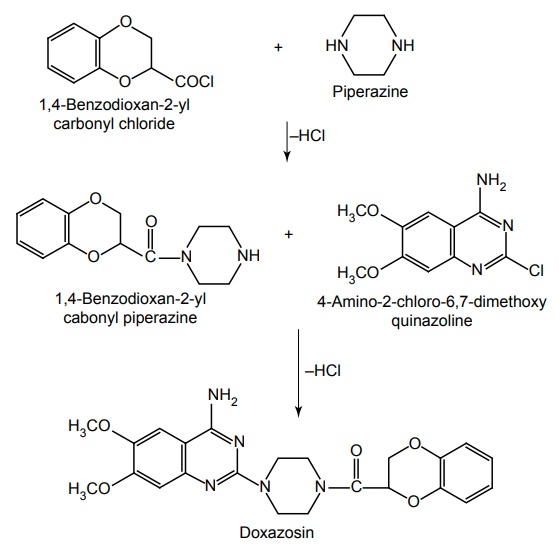
Properties and uses: It is a water soluble analogue of prazosin and terazosin. It is a white or almost white crystalline powder. It shows polymorphism and some forms may be hygroscopic. Slightly soluble in water, methanol, insoluble in acetone, but soluble in a mixture of water and tetrahydrofuran. It is a new selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist similar to prazosin. Doxazosin, possibly, may prevent influx of extracellular calcium and cause relaxation of vascular smooth muscle. Headache and dizziness are the two most prevalent adverse effects.
Assay: It is assayed by using liquid chromatography technique.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dose: For hypertension: For adult as mesylate, initial dose is 1 mg at bed time increase after 1–2 week according to response. Maintenance dose is 4 mg once daily, maximum dose is 16 mg/ day.
Related Topics
