4-Substituted Quinolines: Structure Activity Relationship
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antimalarials
At C-4 position, the dialkylaminoalkyl side chain has 2-5 carbon atoms between the nitrogen atoms, particularly the 4-diethylaminomethyl butyl amino side chain that is optimal for activity, as in chloroquine and quinacrine.
STRUCTURE–ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP
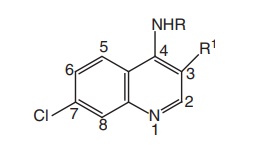
·At C-4 position, the dialkylaminoalkyl side
chain has 2-5 carbon atoms between the nitrogen atoms, particularly the 4-diethylaminomethyl
butyl amino side chain that is optimal for activity, as in chloroquine and
quinacrine.
·The substitution of a hydroxyl group on one of
the ethyl groups on the tertiary amine (hydroxyl quinoline), reduces toxicity.
·Incorporation of an aromatic ring in the side
chain (e.g. amodiaquine) gives a compound with reduced toxicity and activity.
·The tertiary amine in the side chain is
important.
·The introduction of an unsaturated bond in the
side chain was not detrimental to activity.
·The 7-chloro group in the quinoline nucleus is
optimal, the methyl group in position 3 reduces activity, and an additional
methyl group in position 8 abolishes activity.
·The D-isomer of chloroquine is less
toxic than its L-isomer.
