Quassia
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Glycosides
Quassia is dried wood of the stem of Aeschrion excelsa (Picroena excelsa Lindl or Picrasma excelsa (S.W) Planchon), belonging to family Simarubaceae.
QUASSIA
Synonyms
Lignum quassiae, Bitter Wood, Jamaica Quassia, Bitter Ash.
Biological Source
Quassia is dried wood of the stem of Aeschrion excelsa (Picroena
excelsa Lindl or Picrasma excelsa
(S.W) Planchon), belonging to family Simarubaceae.
Geographical Source
It is indigeneous to West Indies, Jamaica, Barbados,
Martinique and St. Vincent.
Cultivation and Collection
It is a tree growing 50–100 feet, erect stem over 3 feet in
diameter. The stem is cut and small branches are separated. Main trunk and
large branches are cut in to small pieces, sewed and logs and billets prepared.
Bark is removed from logs and billets and shavings, raspings and chips made and
then dried immediately to prevent the growth of moulds.
Characteristics
It is in the form of chips or raspings, Chips are
poanoconvex, has no smell but an intense bitter taste. They have false annual
rings breaking easily longitudinally. Colour is white, but changes to yellow on
contact with the air. Cork easily detaches from phloem. Sometimes black
markings are present because of mould.

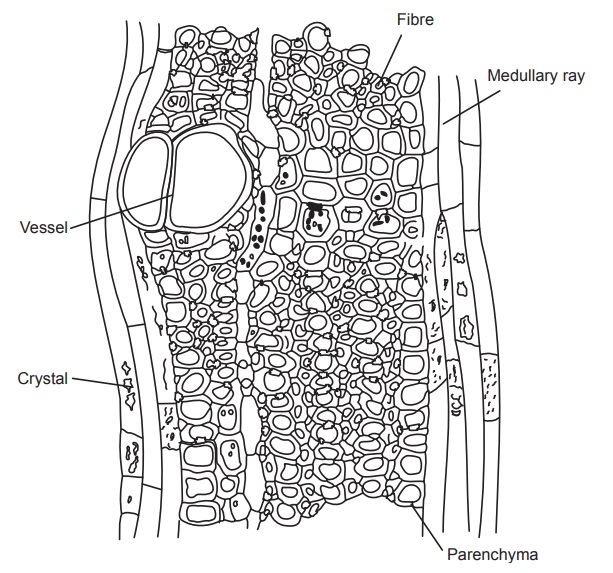
Microscopy
Wood consists of medullary rays, parenchyma and vessels. The
whole drug is stained red with phloroglucinol and hydrochloric acid due to the
presence of lignin in the cell wall. Medullary rays are one to five seriate but
usually triseriate. Cells of medullary rays are radially elongated and their
cell walls are pitted. Vessels are thick walled and are border pitted. Fibres
are also present in the wood; they are long; tapering, thick walled with
oblique shaped pits. Prismatic type of calcium oxalate is present in cells of
medullary rays and parenchyma.
Chemical Constituents
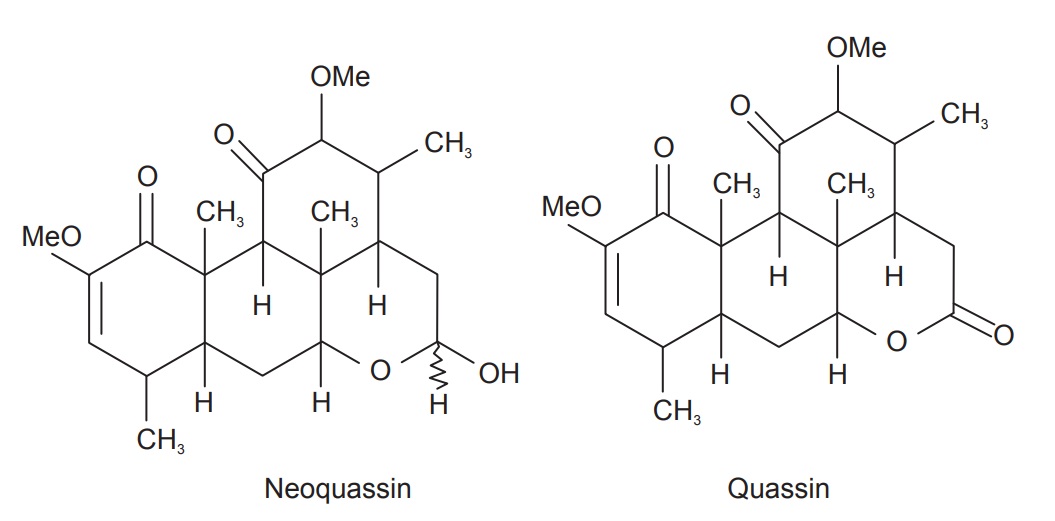
Quassia contains bitter amaroid compounds like quassin,
isoquassin (picrasmin), neoquassin and 18-hydroxy quassin. Volatile oil, gummy
extractive pectin, woody fibre, tartrate and sulphate of lime, chlorides of
calcium and sodium, various salts such as oxalate and ammoniacal salt, nitrate
of potash and sulphate of soda are also present.
Uses
Quassia wood is a pure bitter tonic and stomachic; it is
also a vermicide and slight narcotic; it acts on flies and some of the higher
animals as a narcotic poison. It is a valuable remedy in convalescence, after
acute disease and in debility and atonic dyspepsia; an antispasmodic in fever.
In small doses Quassia increases the appetite.
Allied Drugs
Quassia amara, or Surinan Quassia (Simarubaceae),
is in much smaller billets than the
Jamaica Quassia, and is used in its place on the Continent, and is easily
recognized from the Jamaica one, which it closely resembles, by its medullary
rays, which are only one cell wide, and contain no calcium oxalate.
