Polypeptide antibiotics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
The compounds have complex polypeptide structure. These are resistant to animal and plant proteases.
Polypeptide antibiotics
The
compounds have complex polypeptide structure. These are resistant to animal and
plant proteases. These contain lipid moieties besides amino acids that are not
found in peptides of animal and plant origins. Examples: bacitracin, polymycin,
amphomycin, tyrothricin, and vancomycin.
i. Bacitracin
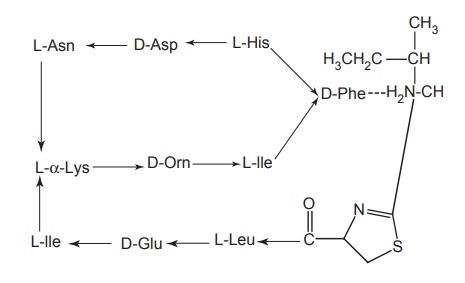
Properties and uses: Bacitracin is a white hygroscopic powder,
soluble in water and alcohol. Bacitracin antibiotic is isolated from the
fermentation broth of a culture of tracyl-1 strain of Bacillus subtilis. It is found to be a complex mixture of at least
10 polypeptides (A, A1, B, C, D, E, F1, F2, F3,
and G), of which bacitracin A fraction is believed to be the most abundant and
the most potent. A divalent ion Zn++ enhances its activity. Although bacitracin
is occasionally employed for topical application (often in combination with
neomycin, polymycin, and tyrothicin) for the treatment of burns, ulcer, and
wounds, it can cause serious necrosis of the kidney tubules; if it is given
systematically (i.e. I.V route) an oral administration is not feasible due to
its lack of absorption from the GI tract. A variety of gram-positive cocci and bacilli are sensitive to bacitracin. It should be stored in
airtight containers due to its hygroscopic nature.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
ii. Polymyxin
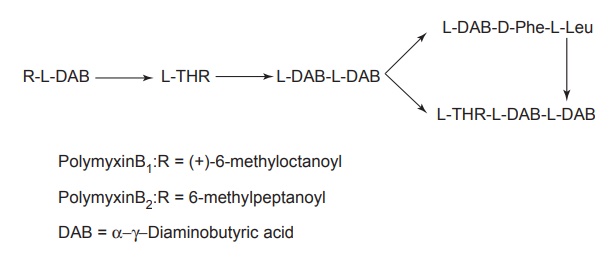
Properties and uses: Polymycin sulphate is a white hygroscopic
powder, soluble in water, and slightly soluble in ethanol. The polymyxins are
cyclic peptides holding a fatty acid side chain. This is a group of relatively
simple basic, cationic, detergent peptides that are produced by Bacillus polymyxia. At least, five
polymyxins (A, B, C, D, and E) are known, but only polymyxin B and polymyxin E
are of clinical utility. Both polymyxin B and polymyxin E (colistin) are
mixtures of two components and is used in the treatment of bacterial
meningitis, urinary tract infection, burns, wounds, and gastroenteritis.
Polymyxin may affect renal tubules and central nervous system (CNS), and
because of their nephrotoxicity associated with their systemic use, they are
primarily employed to treat topical infections.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Related Topics
