Plateau Principle
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Pharmacokinetics; Metabolism Excretion Of Drugs, Kinetics Of Elimination
When constant dose of a drug is repeated before the expiry of 4 t½, it would achieve higher peak concentration, because some remnant of the previous dose will be present in the body. This continues with every dose until progressively increasing rate of elimination (which increases with increase in concentration) balances the amount administered over the dose interval.
PLATEAU PRINCIPLE
When
constant dose of a drug is repeated before the expiry of 4 t½, it would achieve
higher peak concentration, because some remnant of the previous dose will be
present in the body. This continues with every dose until progressively
increasing rate of elimination (which increases with increase in concentration)
balances the amount administered over the dose interval. Subsequently plasma
concentration plateaus and fluctuates about an average steadystate level. This
is known as the plateau principle of drug accumulation. Steadystate is reached
in 4–5 half lives unless dose interval is very much longer than t½ (Fig. 3.6).
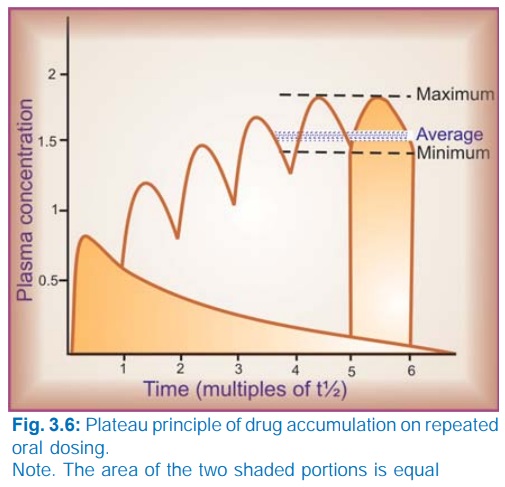
The amplitude of
fluctuations in plasma concentration at steadystate depends on the dose interval
relative to the t½, i.e. the difference between the maximum and minimum levels
is less if smaller doses are repeated more frequently (dose rate remaining
constant). Dose intervals are generally a compromise between what amplitude of
fluctuations is clinically tolerated (loss of efficacy at troughs and side
effects at peaks) and what frequency of dosing is convenient. However, if the
dose rate is changed, a new average Cpss
is attained over the next 4–5 half lives. When the drug is administered orally
(absorption takes some time), average Cpss
is approximately 1/3 of the way between the minimal and maximal levels in a
dose interval.
