Oleander
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Glycosides
It consists of the dried seeds and leaves of Nerium indicum Linn, belonging to family Apocynaceae.
OLEANDER
Biological Source
It consists of the dried seeds and leaves of Nerium indicum Linn, belonging to family
Apocynaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in the United States, India, West Indies.
Characteristics
Leaves exstipulate, linear, lanceolate 10–20 cm long and up
to 2.5 cm wide, thick, dark green and shining above and dotted beneath.
Microscopy
Lamina shows an isobilateral structure, 3–4 layered palisade
parenchyma cells below upper and above lower epidermis in the mesophyll, single
layer of epidermis covered externally by thick cuticle, epidermal cells
elongate to form unicellular, nonlignified and nonglandular hairs; four to
seven layers of collenchymatous cells and a wide zone of parenchyma follows the
epidermis; parenchymatous cells thin walled, more or less isodiametric with
intercellular spaces, some cells contain rosette crystals of calcium oxalate; petiole
receives three vascular bundles from stem, central one large and crescent
shaped while other two much smaller and somewhat circular present on each side
of central vascular bundle. The leaves contain anomocytic type of stomata.
Chemical Constituents
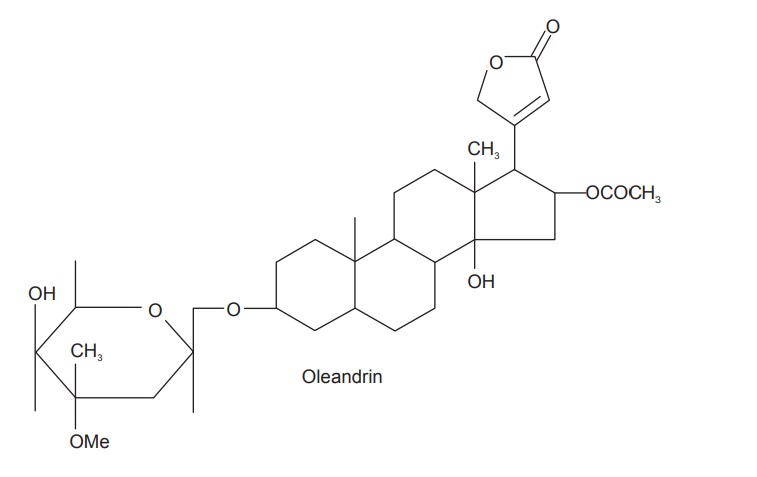
Cardiac glycosides oleandrine, gitoxigenin, neridiginoside,
adynerigenin, etc., also it contains terpenoids, sterols, tannins, essential
oils.
Uses
Leaves are used in cutaneous eruptions. The paste of the
root is applied externally in haemorrhoides and ulcerations.
