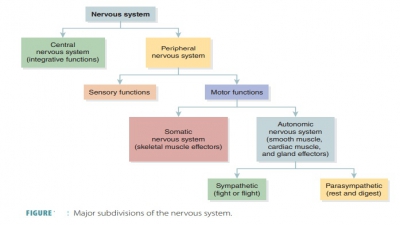
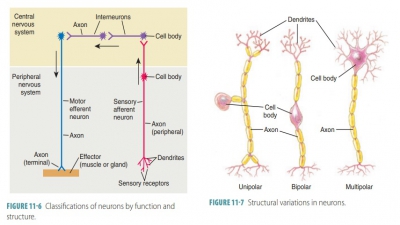
Nerve Impulses
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Control and Coordination: Neural Tissue
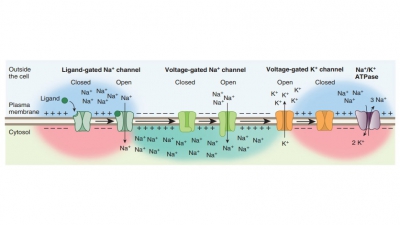
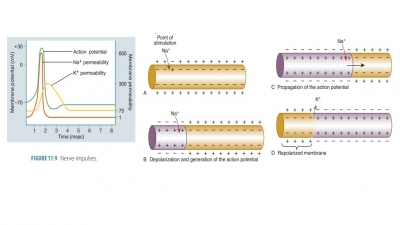
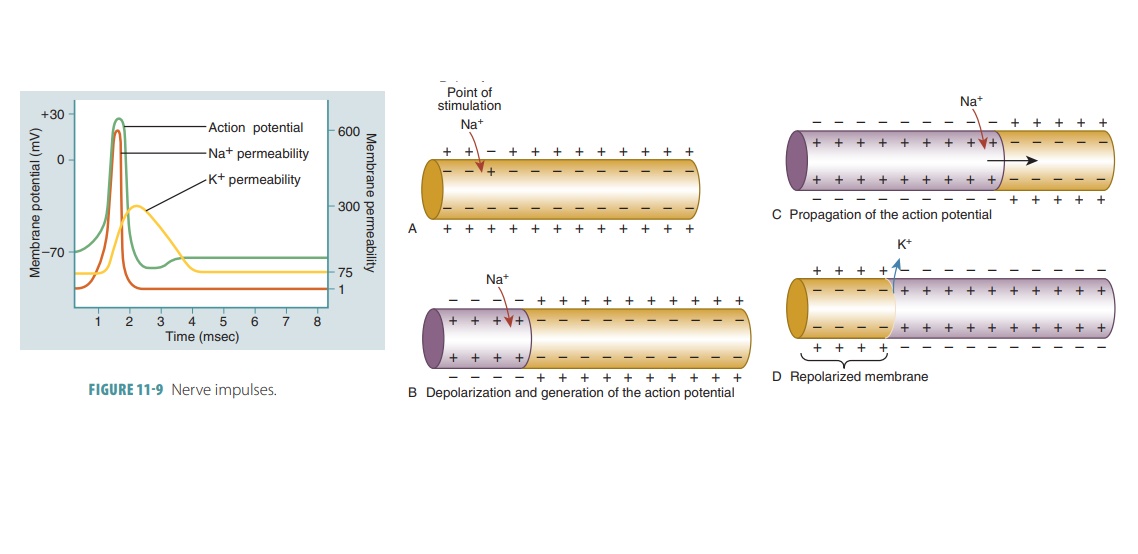
In a nerve cell membrane, an action potential causes a local bioelectric current to reach other portions of the membrane.
Nerve Impulses
In a nerve cell membrane, an
action potential causes a local bioelectric current
to reach other portions of the membrane. This stimulates the adjacent mem-brane
to its threshold level and another action poten-tial is triggered, stimulating
yet another region. These action potential waves move down to the end of the
axon, constituting nerve impulses (FIGURE 11-9).
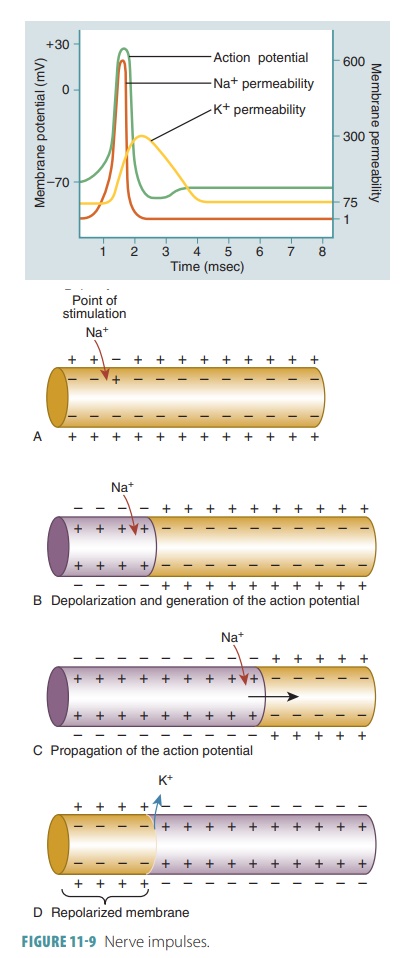
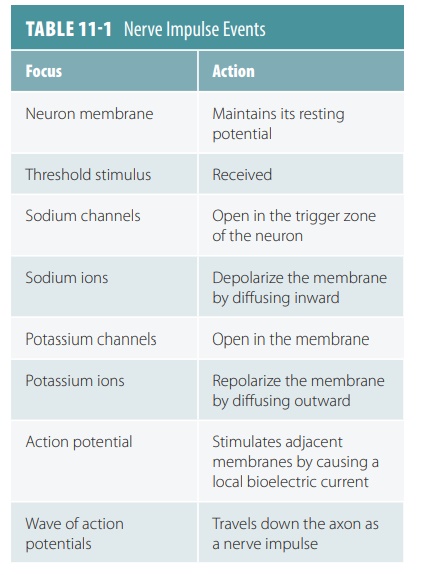
TABLE 11-1 describes the steps in the conduction of a nerve impulse. A
membrane’s resistance is defined as
the level at which it restricts signal or ion movement.
Impulses are conducted over the
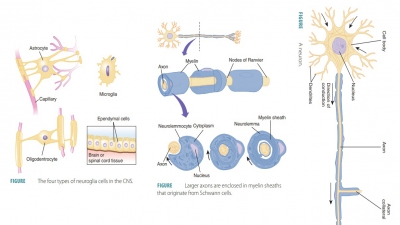
entire surface of unmyelinated axons. Myelinated axons are insulated by their
myelin content, reducing impulse conduction. The myelin sheath is interrupted
by nodes of Ranvier between the Schwann cells, meaning action poten-tials occur
at the nodes. Therefore, nerve impulses on myelinated axons appear to move from
node to node. This saltatory impulse conduction is much faster than unmyelinated
axon conduction. The greater the diam-eter of the axon, the quicker the
impulses are con-ducted. For example, the extremely fast conduction on a
skeletal muscle as compared with much slower conduction on a sensory neuron.
Nerve impulses are conducted
either completely or not at all, known as the all-or-none response. All impulses on an axon are of the same
strength. If stimula-tion is raised, the impulses remain the same in strength
but occur more rapidly. After each nerve impulse, a very brief refractory
period limits the frequency of further nerve impulses. Most of the time, axons
con-duct impulses at the speed of 100 per second, although speeds of as high as
700 per second are possible.