Ion Channels
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Pharmacodynamics Mechanism Of Drug Action; Receptor Pharmacology
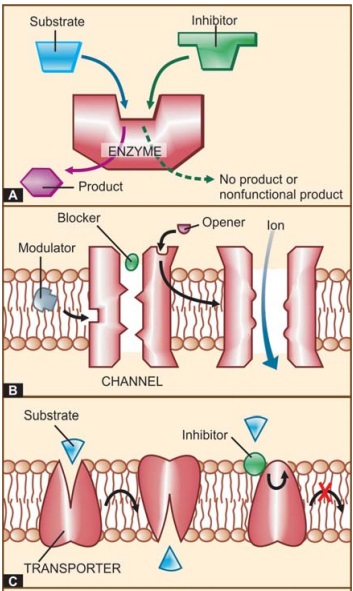
Proteins which act as ion selective channels participate in transmembrane signaling and regulate intracellular ionic composition. This makes them a common target of drug action
ION CHANNELS
Proteins which act as
ion selective channels participate in transmembrane signaling and regulate
intracellular ionic composition. This makes them a common target of drug action
(Fig. 4.1B). Drugs can affect ion channels either through specific receptors
(ligand gated ion channels, Gprotein operated ion channels or by directly
binding to the channel and affecting ion movement through it, e.g. local
anaesthetics which physically obstruct voltage sensitive Na+ channels. In addition, certain drugs
modulate opening and closing of the channels, e.g.:
§ Quinidine blocks
myocardial Na+ channels.
§ Dofetilide and
amiodarone block myocardial delayed rectifier K+ channel.
§ Nifedipine blocks Ltype
of voltage sensitive Ca2+ channel.
§ Nicorandil opens ATPsensitive
K+ channels.
§ Sulfonylurea
hypoglycaemics inhibit pancreatic ATPsensitive K+ channels.
§ Amiloride inhibits
renal epithelial Na+ channels.
§ Phenytoin modulates
(prolongs the inactivated state of) voltage sensitive neuronal Na+ channel.
§ Ethosuximide inhibits
Ttype of Ca2+ channels in thalamic neurones