Eucalyptus Oil
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
Eucalyptus oil is the essential oil obtained by the distillation of fresh leaves of Eucalyptus globulus and other species like E. polybractea, E. viminalis, and E. smithii, belonging to family Myrtaceae.
EUCALYPTUS OIL
Synonyms
Eucalyptus, Stringy Bark Tree, Blue gum, Blue Gum Tree.
Biological Source
Eucalyptus oil is the essential oil obtained by the distillation
of fresh leaves of Eucalyptus globulus
and other species like E. polybractea, E.
viminalis, and E. smithii,
belonging to family Myrtaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in Australia, Tasmania, United States,
Spain, Portugal, Brazil, North and South Africa, India, France, and Southern
Europe.
History
Eucalyptus globulus has been used since a long time for intermittent fever. The leaves and
their preparations have been successfully used as a tonic, stimulant,
stomachic, in dyspepsia, in catarrh of the stomach, in typhoid fever, in
asthma, in whooping cough, etc. More recently it has been recommended as a
diuretic in the treatment of dropsy.
Characteristics
Eucalyptus is a tall, evergreen tree, the trunk, which grows
to 300 feet high or more, is covered with peeling papery bark. The leaves on the
young plant, up to five years old, are opposite, sessile, soft, oblong,
pointed, and a hoary blue colour. The mature leaves are alternate, petioled,
leathery, and shaped like a scimitar. The flowers are solitary and white,
without any petals.
Eucalyptus oil is a colourless or straw-coloured fluid, with
a characteristic odour and taste, soluble in its own weight of alcohol.
According to the British Pharmacopoeia Eucalyptus oil should contain not less
than 55%, by volume of Eucalyptol, have a specific gravity 0.910 to 0.930, and
optical rotation –10 degrees to 10 degrees.
Microscopy
Eucalyptus leaf is isobilateral. Stomata are of anomocytic
type and sunken, on both surfaces. Epidermal cells are polygonal with thick
cuticle; anticlinal walls are straight on both surfaces. There are three to
four layers of elongated palisade cells below each epidermis. Between these
palisade regions, two to three layers of spongy parenchyma occur and some of
its cells contain cluster and prismatic calcium oxalate crystals. Palisade
regions exhibit large subglobular oleoresin cavities. The midrib region shows
no collenchymatous cells. Transverse section through the midrib region shows
nearly uninterrupted arc of lignified pericyclic fibres just outside the
vascular bundle.
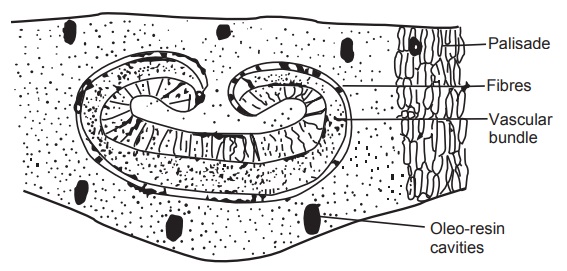 T.S. (schematic) of eucalyptus leaf
T.S. (schematic) of eucalyptus leaf
Chemical Constituents
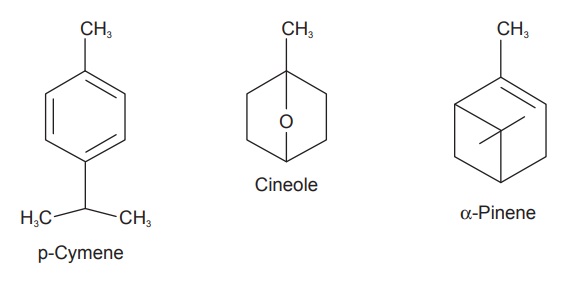
Eucalyptus oil contains volatile oil of which 70 to 85% is
1,8-cineole also known as eucalyptol. The other constituents present are
p-cymene, α-pinene; small quantity of
sesquiterpenes like ledol, aromadendrene; aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols. It
also has polyphenolic acids like ferulic acid, caffeic acid, gallic acid;
flavonoids such as eucalyptin, hyperoside and rutin.
Uses
The oil is used as stimulant, antiseptic, flavouring agent,
aromatic, deodorant, expectorant, antimicrobial, febrifuge, diuretic, and
antispasmodic. It is also used in the treatment of lung diseases, sore throat,
cold, as a vapour bath for asthma and various respiratory ailments and in
bronchitis.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Cold Balm, Muscle and Joint Rub, Canisep, Erina-EP, Scavon Vet. (Himalaya Drug
Company).
