Cotransmission
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Autonomic Nervous System: General Considerations
It has now become apparent that the classical ‘one neurone—one transmitter’ model is an over simplification. Most peripheral and central neurones have been shown to release more than one active substance when stimulated.
COTRANSMISSION
It has now become
apparent that the classical ‘one neurone—one transmitter’ model is an over
simplification. Most peripheral and central neurones have been shown to release
more than one active substance when stimulated. In the ANS, besides the primary
transmitters ACh and NA, neurones have been found to elaborate purines (ATP,
adenosine), peptides (vasoactive intestinal peptide or VIP, neuropeptideY or
NPY, substance P, enkephalins, somatostatin, etc.), nitric oxide and
prostaglandins as cotransmitters. In most autonomic cholinergic neurones VIP is
associated with ACh, while ATP is associated with both ACh and NA. Vascular
adrenergic nerves contain NPY which causes long lasting vasoconstriction. The
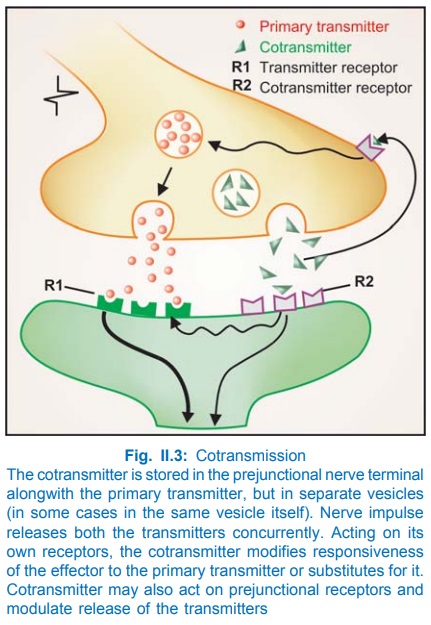
cotransmitter is stored in the same neurone but in distinct synaptic vesicles
or locations (Fig. II.3). However, ATP is stored with NA in the same vesicle.
On being released by the nerve impulse it may serve to regulate the presynaptic
release of the primary transmitter and/or postsynaptic sensitivity to it (neuromodulator
role). The cotransmitter may also serve as an alternative transmitter in its
own right and/or exert a trophic influence on the synaptic structures.
Nonadrenergic,
noncholinergic (NANC) transmission has been demonstrated in the autonomic
innervation of the gut, vas deferens, urinary tract, salivary glands and
certain blood vessels, where nerve stimulation is able to evoke limited responses
even in the presence of total adrenergic and cholinergic blockade. For example,
it has been shown that stimulation of sympathetic nerve to guinea pig vas
deferens elicits a biphasic contractile response, the initial shortlasting
phase of which is mediated by ATP (through P2 receptors) and the second longer
lasting phase by NA (through α1 receptors). Many
anomalous findings have been explained by the revelation of cotransmission.
Related Topics
