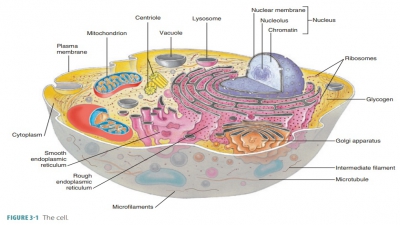
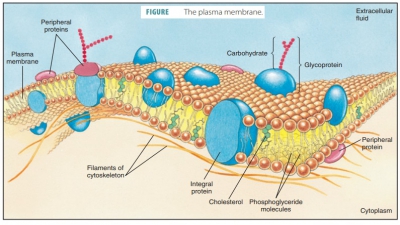
Cells
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Levels of Organization : Cells
Cells are the building blocks of all plants and animals. All cells come from the division of preexisting cells.
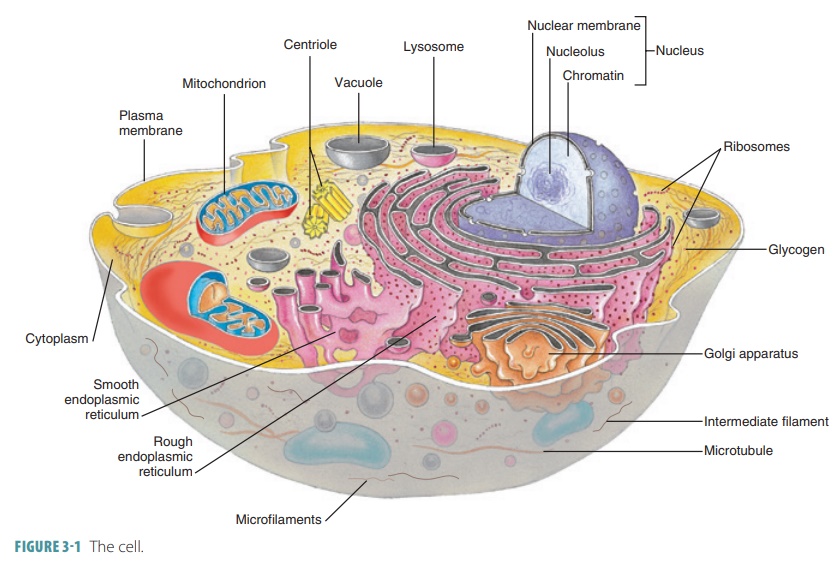
Cells
After
studying this chapter, readers should be able to
1. Explain
the parts of a cell’s structure.
2. Describe
the structure and function of the cell membrane.
3. Describe
the structure and function of cytoplasm and cytosol.
4. Describe
the parts of the cell nucleus and their functions.
5. Describe
the “powerhouses” of the cell.
6. Describe
the processes that transport substances across the plasma membrane.
7. Compare
and define cilia and flagella.
8. Compare
passive and active cell mechanisms.
9. Describe
gene activation in protein synthesis.
10. Explain
cell division and cancer.
Overview
Cells are the building blocks of all plants and ani-mals. All cells come from the division of preexisting cells. They are the smallest units of the body that per-form all vital physiological functions. Approximately, 75 trillion cells exist in an adult human being. Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level. Cells have different sizes, shapes, and forms, depending on their functions. Today, the study of cellular structure and function or cytology is part of the broader disci-pline of cell biology, which includes aspects of biology, chemistry, and physics.
Related Topics