Capsules
| Home | | Pharmaceutical Drugs and Dosage | | Pharmaceutical Industrial Management |Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drugs and Dosage: Capsules
Capsules are the dosage forms in which the drug formulation in a powder, semisolid, or liquid form is enclosed in a shell.
Capsules
Introduction
Capsules
are the dosage forms in which the drug formulation in a powder, semisolid, or
liquid form is enclosed in a shell. This shell is generally made from gelatin,
but can be made from other polymers such as hydroxypro-pyl methylcellulose
(HPMC), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), seaweed, or starch. Depending on the
composition of the gelatin shell, the capsules can be hard or soft gelatin
capsules. Soft gelatin capsules (also known as softgels) are made from a relatively more flexible, plasticized
gelatin film than hard gela-tin capsules. Hard capsules, such as hard gelatin
or HPMC capsules, are typically used for powder or solid fills, whereas soft
gelatin capsules are used for semisolid or liquid fills. Lately, hard capsules
have also been used for liquid or semisolid fills.
Most
soft and hard capsules are intended to be swallowed as a whole. Some soft
gelatin capsules are intended for rectal or vaginal insertion as suppositories.
Some soft gelatin capsules are intended to be cut open by the patient to remove
and externally apply the contained medicament, for
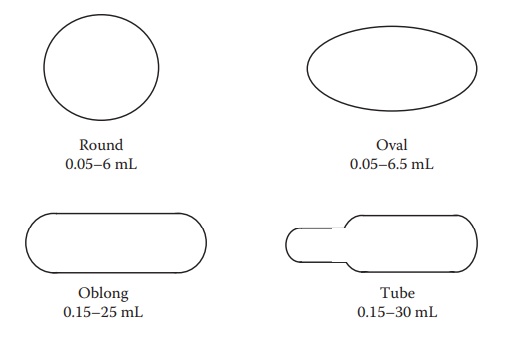
Figure 21.1 Schematic diagrams illustrating different shapes of soft gelatin capsules. The range of fill volumes is also indicated.
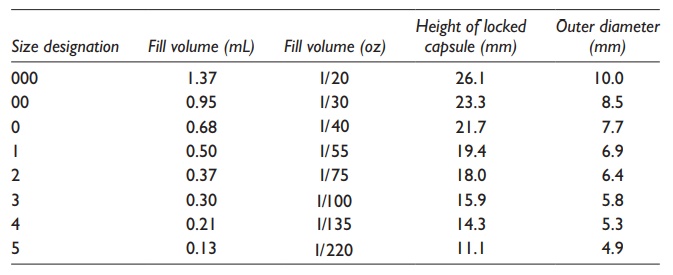
Table 21.1 Typical sizes of hard gelatin
capsules
The
capsule shell dissolves rapidly on contact with gastrointestinal (GI) fluids,
thus releasing the capsule’s contents. Drug’s bioavailability from capsules is
usually high and similar to those of immediate-release (IR) tablets. Coating of
capsule shell or drug particles (within the capsule) with sustained-release
(SR) polymers can prolong drug release and affect bioavailability.
Hard
gelatin capsules have a significant amount of bound water. These capsules are
generally not physically stable in low humidity conditions, such as in the
presence of desiccant in the packaged drug product. They tend to become fragile
and crack at low humidity. On the other hand, HPMC capsules have lower
equilibrium moisture contents than gelatin capsules and have better physical
stability (i.e., do not become fragile and crack) on exposure to low humidity.
The majority of capsule products manufactured today are hard gelatin capsules.
Related Topics