Boron
| Home | | Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry |Chapter: Essentials of Inorganic Chemistry : The Boron Group - Group 13
Boric acid is a long-standing traditional remedy with mainly antifungal and antimicrobial effects. For medic-inal uses, it has become known as sal sedativum, which was discovered by Homberg, the Dutch natural philosopher, in 1702 .
Boron
Introduction
Boron has the atomic number 5 and the symbol B, and is a so-called
metalloid (see Chapter 4). Boron compounds have been known for many centuries
and especially used in the production of glass. Boric acid [B(OH)3]
is used in the large-scale production of glass. Borosilicate glasses (Pyrex®
glass), which are pro-duced by a fusion of B2O3 and
silicate, are extremely heat resistant and often used in laboratories.
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, it was recognised
that boron is an essential micronutrient for plants. A deficiency of boron can
lead to deformation in the vegetable growth such as hollow stems and hearts.
Furthermore, the plant growth is reduced and fertility can be affected. In
general, boron deficiency leads to qualitative and quantitative reduction in
the production of the crop. Boron is typically available to plants as boric
acid [B(OH)3] or borate [B(OH)4]−. The exact
role of boron in plants is not understood, but there is evidence that it is
involved in pectin cross-linking in primary cell walls, which is essential for
normal growth and development of higher plants.
Borax (Na2[B4O5(OH)4]⋅8H2O) can be applied as a fertiliser and, together with kernite (Na2[B4O5(OH)4]⋅2H2O), forms the two most commercially available borates. Borates find a wide range of practical applications such as in detergents, cosmetics, antifungal mixtures as well as components in fibreglass and others.
The toxicity of borates in mammals is
relatively low, but it exhibits a significantly higher risk to arthropods and
can be used as an insecticide.
Boron-based compounds are used in a wide range of clinical applications
including their use as antifun-gal and antimicrobial agent, as proteasome
inhibitors and as a noninvasive treatment option for malignant tumours. The
latter application will be discussed in the chapter on radiopharmaceuticals
(Chapter 10).
Pharmaceutical
applications of boric acid
Boric acid is a long-standing traditional remedy with mainly
antifungal and antimicrobial effects. For medic-inal uses, it has become known
as sal sedativum, which was
discovered by Homberg, the Dutch natural philosopher, in 1702 . Diluted
solutions were and sometimes still are used as antiseptics for the treatment of
athletes’ foot and bacterial thrush, and in much diluted solutions as eyewash
(Figure 4.3) .
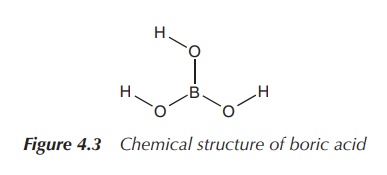
Boric acid can be prepared by reacting borax with a mineral acid:
Na2B4O7 ⋅ 10H2O + 2HCl →
4B(OH)3[or H3BO3] + 2NaCl + 5H2O
In general, there are many other health claims around the
clinical use of boric acid and boron-containing compounds, but many of those
have no supporting clinical evidence.
Bortezomib
Bortezomib belong to the class of drugs called proteasome inhibitors and is licensed in
the United States and the United Kingdom for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
The drug has been licensed for patients in whom the myeloma has progressed
despite prior treatment or where a bone marrow transplant is not possible or
was not successful. It is marketed under the name Velcade® or
Cytomib®. Velcade is administered via injection and is sold as
powder for reconstitution (Figure 4.4) .
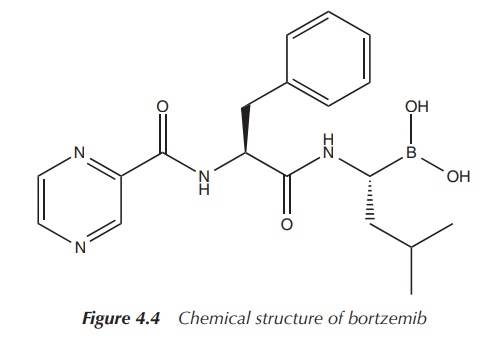
Bortezomib was the first drug approved in the new drug class of
proteasome inhibitors and boron seems to be its active element. For the mode of
action, it is believed that the boron atom binds with high affinity and
specificity to the catalytic site of 26S proteasome and inhibits its action.
Therapy with Bortezomib can lead to a variety of adverse reactions, including
peripheral neuropathy, myelosuppression, renal impairment and gastrointestinal
(GI) disturbances together with changes in taste. Nevertheless, the side
effects are in most cases less severe than with alternative treatment options
such as bone marrow transplantation .
Related Topics
