Aminoglycoside antibiotics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
a. Streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin b. Gentamycins c. Neomycin d. Kanamycin e. Amikacin f. Tobramycin g. Netilmicin (1-N-ethylsisomicin)
Aminoglycoside antibiotics
The
aminoglycoside antibiotics contain one or more amino sugars linked to an
aminocytitol ring by glycosidic bonds. These are broad-spectrum antibiotics; in
general, they have greater activity against gram-negative than gram-positive
bacteria. The development of streptomycin, the first antibiotic of this group,
was a well-planned work of Waksman (1944) and his associates, who isolated it
from a strain of Streptomyces griseus.
The
aminoglycoside can produces severe adverse effects, which include nephrotoxity,
ototoxicity, and neuro effects. These properties have limited the use of
aminoglycoside chemotherapy to serious systemic indications. Some
aminoglycosides can be administered for ophthalmic and topical purposes.
Mode of action: The aminoglycosides exhibit bactericidal effects
as a result of several phenomena. Ribosomal binding on 30s and 50s subunits as
well as the interface produces misreading; this disturbs the normal protein
synthesis. Cell membrane damage also plays an integral part in ensuring
bacterial cell death. Some examples of aminoglycoside antibiotics are listed in
Table 4.1.
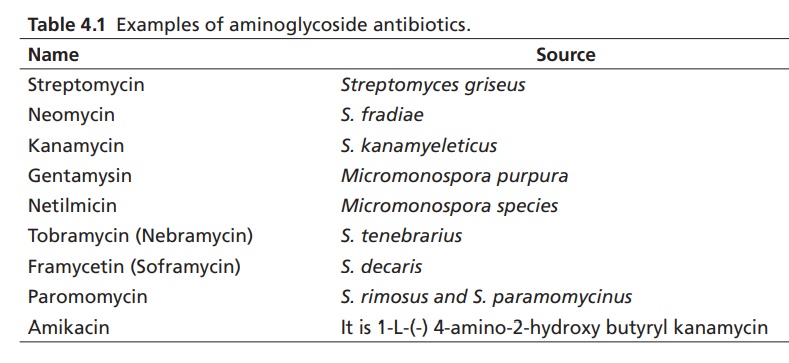
a. Streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin
Properties and uses: Streptomycin sulphate is a white hygroscopic
powder, very soluble in water, and practically insoluble in ethanol. The
organism, S. griseus, releases the other
substances, such as hydroxystreptomycin, mannisidostreptomycin, and
cycloheximide, but do not reach up to the required activity/potency level. The
development of resistant strains of bacteria and chronic toxicity constitutes
major drawbacks of this category. It is an aminoglycoside antibacterial also
used as an antitubercular drug.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
Dosage forms: Streptomycin injection B.P.
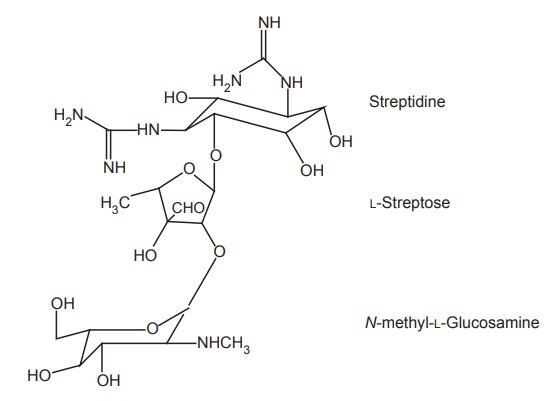
b. Gentamycins
Properties and uses: Gentamycin is a mixture of C1, C2,
and C1A compounds, obtained commercially from Micromonospora purpurea. Gentamycin sulphate exists as white
hygroscopic powder, soluble in water, and practically insoluble in alcohol,
although it is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is used in the treatment of
infections caused by gram-negative bacteria of particular interest and has a
high degree of activity against
P. aeruginosa, where the important causative factor is burned skin. It is
used topically in the treatment of infected bed-sores, pyodermata, burns, and
in the eye infection.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
Dosage forms: Gentamicin cream B.P., Gentamicin ear drops B.P., Gentamicin and
Hydrocortisone acetate ear drops B.P., Gentamicin eye drops B.P., Gentamicin
injection B.P., Gentamicin ointment B.P.
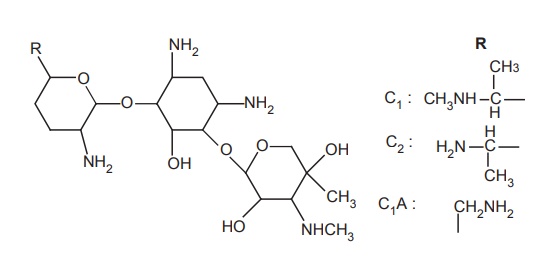
c. Neomycin
Properties and uses: Neomycin sulphate is a white or yellowish-white
hygroscopic powder, very soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol,
and practically insoluble in acetone. Neomycin is a mixture of closely related
epimers, neomycin B, and C. Neomycin B differ from neomycin C by the nature of
the sugar attached terminally to D-ribose, this sugar called
neosamine. B1 differs from neosamine C in its stereochemistry. In neomycin B1
, the neobiosamine moiety contains. β-L-iodopyranosyl, whereas in
neomycin C the configuration is inverted and it is 2-D-glucopyranosyl.
It is photosensitive and its main use is in the treatment of the ear, eye, and
skin infections; these include burns, wounds, ulcer, and infected dermatoses.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
Dosage forms: Dexamethasone and Neomycin ear spray B.P., Hydrocortisone and
neomycin cream B.P., Hydrocortisone acetate and Neomycin ear drops B.P., Hydrocortisone
acetate and Neomycin eye drops B.P., Neomycin eye drops B.P., Hydrocortisone
acetate and Neomycin eye ointment B.P., Neomycin eye ointment B.P., Neomycin
oral solution B.P., Neomycin tablets B.P.
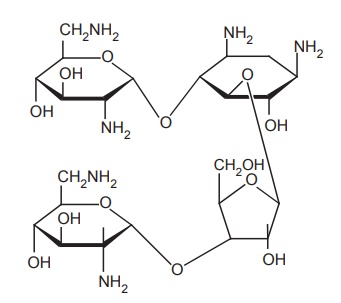
d. Kanamycin
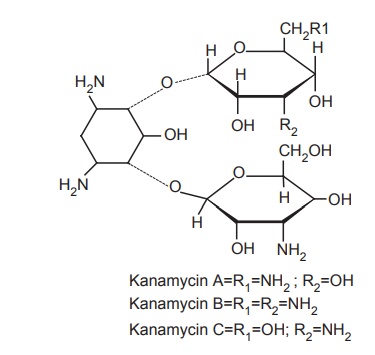
Properties and uses: Kanamycin sulphate is a white crystalline powder,
soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in alcohol. The mixture
consists of three related structures, that is, Kanamycin A, B, and C. The kanamycins do not possess D-ribose
molecule that is present in neomycins and paramomycins. The use of kanamycins
is restricted to infections of the intestinal tract and to systemic infections.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
e. Amikacin
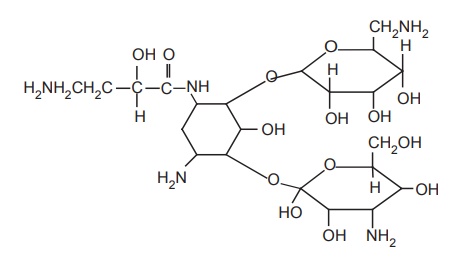
Properties and uses: Amikacin is a semisynthetic drug derived form
kanamycin A. It retains 50% of the original activity of kanamycin A. L-Isomer
is more active than D-isomer. It resists attack by most
bacterialinactivating enzyme. Therefore, it is very effective and less ototoxic
than other aminoglycosides.
Dosage forms: Amikacin sulphate injection I.P.
f. Tobramycin
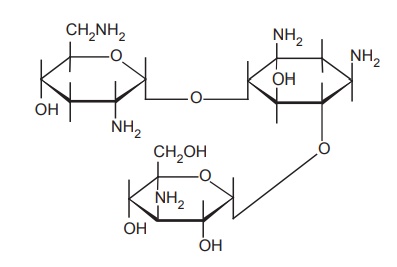
Properties and uses: Its activity is similar to gentamycin. The
superior activity of tobramycin against P.
aeruginosa may make it useful in the treatment of bacterial
oesteromyelitis, and pneumonia caused by P.
species.
Dosage forms: Tobramycin injection I.P.
g. Netilmicin (1-N-ethylsisomicin)
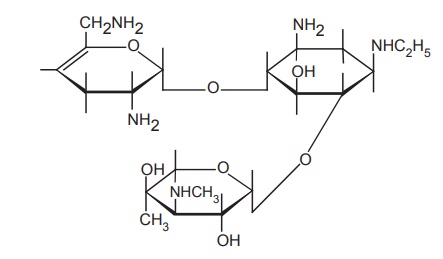
Properties and uses: Netilimycin sulphate is a white or
yellowish-white hygroscopic powder, very soluble in water, practically
insoluble in acetone and alcohol. It is similar to gentamycin and tobramycin.
The majority of the aminoglycoside inactivating enzymes do not metabolize it.
It is useful for the treatment of serious infections due to susceptible
enterobacteria and other aerobic gram-negative bacilli.
Assay: It is assayed by microbiological method.
Related Topics
