Actions of 5 Hydroxytryptamine
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : 5Hydroxytryptamine, Its Antagonists And Drug Therapy Of Migraine
5HT is a potent depolarizer of nerve endings. It thus exerts direct as well as reflex and indirect
ACTIONS
5HT is a potent
depolarizer of nerve endings. It thus exerts direct as well as reflex and indirect
5HT1 : Autoreceptors; inhibit serotonergic neural activity in brain.
5HT1A—present in raphe
nuclei and hippocampus; buspirone may act through these receptors.
5HT1B/1D—Constricts cranial
blood vessels and inhibits release of inflammatory neuropeptides in them;
sumatriptan acts through these receptors.
5HT2A : Previously D type receptor; most important postjunctional
receptor mediating direct actions of 5HT like vascular and visceral smooth muscle
contraction, platelet aggregation, neuronal activation in brain; ketanserin
blocks these receptors.
5HT3 : Previously M type receptor; depolarizes neurones by
gating cation channels; elicits reflex effects of 5HT—emesis, gut peristalsis,
bradycardia, transient hypotension, apnoea, pain, itch; ondansetron acts by
blocking these receptors.
5HT4 : Mediate intestinal secretion, augmentation of
peristalsis. Renzapride is a selective 5HT4 agonist effects.
Tachyphylaxis is common with repeated doses of 5HT. The overall effects
therefore are often variable.
CVS
Arteries are constricted (by action on smooth muscle) as well as dilated (through
EDRF release) by direct action of 5HT, depending on the vascular bed and the
basal tone. In addition, 5HT releases Adr from adrenal medulla, affects
ganglionic transmission and evokes cardiovascular reflexes. The net effect is
complex. Larger arteries and veins are characteristically constricted. In the
microcirculation 5HT dilates arterioles and constricts venules: capillary
pressure rises and fluid escapes. The direct action to increase capillary
permeability is feeble.
Isolated
heart is stimulated by 5HT: both directly and by release of NA from nerve
endings. In intact animals, bradycardia is mostly seen due to activation of
coronary chemoreflex (Bezold Jarisch reflex) through action on vagal afferent
nerve endings in the coronary bed, evoking bradycardia, hypotension and apnoea.
BP:
a triphasic response is classically seen on i.v. injection of 5HT in animals.
Early sharp fall in
BP—due to coronary chemoreflex.
Brief rise in BP—due
to vasoconstriction and increased cardiac output.
Prolonged
fall in BP—due to arteriolar dilatation and extravasation of fluid.
However,
5HT is not involved in the physiological regulation of BP.
Smooth Muscles
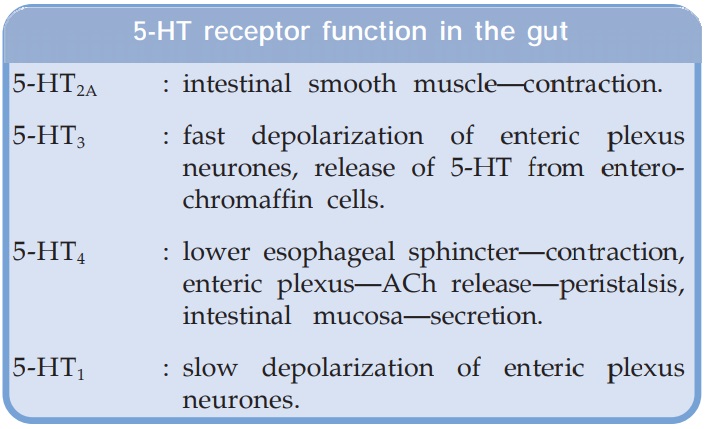
5HT is a potent stimulator of g.i.t., both by direct action as well
as through enteric plexuses. Several subtypes of 5HT receptors are present in
the gut (See box). Peristalsis is
increased and diarrhoea can occur (also due to increased secretion). It
constricts bronchi, but is less potent than histamine. Action on other smooth
muscles in man are feeble and inconsistent.
Glands
5HT inhibits gastric secretion (both acid and pepsin), but increases mucus
production. It thus has ulcer protective property. Effect on other glandular secretions
is not significant.
Nerve Endings And Adrenal Medulla
Afferent nerve endings are
activated—tingling and pricking sensation, pain. Depolarization of visceral afferents
elicits respiratory and cardiovascular reflexes, nausea and vomiting. 5HT is less
potent than histamine in releasing CAs from adrenal medulla.
Respiration
A brief stimulation of respiration (mostly
reflex from bronchial afferents) and hyperventilation are the usual response,
but large doses can cause transient apnoea through coronary chemoreflex.
Platelets
5HT causes changes in shape of platelets and is a
weak aggregator through 5HT2A receptors. However, it does not induce
the release reaction.
CNS
Injected i.v., 5HT does not produce central effects because it poorly crosses bloodbrain
barrier. However, it serves as a transmitter, primarily inhibitory. Direct
injection in the brain produces sleepiness, changes in body temperature, hunger
and a variety of behavioural effects.
Related Topics
