Aconite
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
Aconite is the dried roots of Aconitum napellus Linn, collected from wild or cultivated plants., belonging to family Ranunculaceae.
ACONITE
Synonyms
Monkshood, Friar’s cowl; Mouse-bane; Aconite root;
Mit-hazahar (Hindi); Radix aconiti.
Biological Source
Aconite is the dried roots of Aconitum napellus Linn, collected from wild or cultivated plants.,
belonging to family Ranunculaceae.
Geographical Source
The plant has been originated from the mountaneous and
temperate regions of Europe, It occurs in Alps and Carpathian mountains, hills
of Germany and Himalayas. The greater part of the commercial drug is derived
from wild plant grown in central and southern Europe, particularly Spain.
Cultivation and Collection
Aconite is a perennial herb with a fusiform tuberous root.
The plant is propagated from the daughter tubers. An apical bud on the apex and
six lateral buds on its surface are developed. A lateral shoot bearing a thin
lateral root is produced from each lateral bud. The lateral roots are called
daughter roots and the main root is known as parent root.
The daughter root develops gradually, becomes thick in
autumn and buds are produced on its apex and surface.
Daughter roots are pianted in soil containing leaf mould and
some amount of lime. The roots are collected in autumn. Collection of Aconite
from wild plants is done during flowering season. Roots are dried at 40–50°C.
Thus Aconite arises from one or more lateral shoots which develop into conical
daughter tubers.
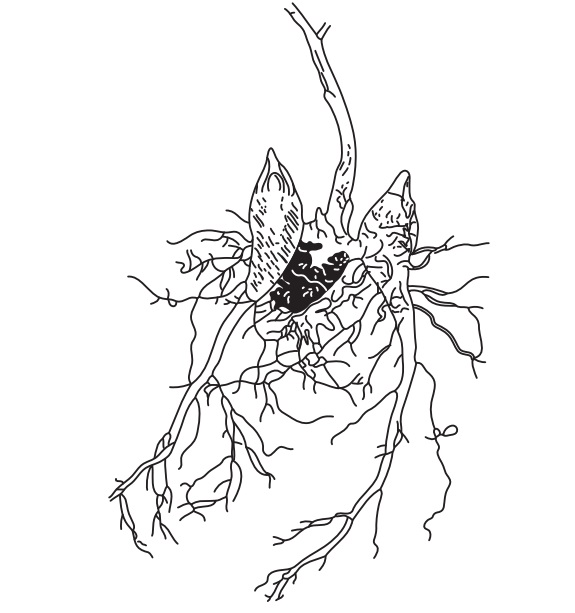
Morphology
Appearance of Aconite varies from season to season. Aconite
collected in autumn is conical in shape and tapering below. Surface is slightly
twisted bearing longitudinal ridges. Some Aconites may contain fibrous rootlets
or their scars. On the top of parent root some remains of stem base are present
which are more shrivelled. An apical bud is present at the apex. The colour is
dark-brown. The root is 4–10 cm in length and 1–3 cm in diameter at the crown.
Rootlets may be present. The fracture is short and starchy. The fractured
surface is five to eight angled, contains stellate cambium and a central pith.
The odour is slight. Taste is sweet at first followed by tingling and numbness.
Chemical Constituents
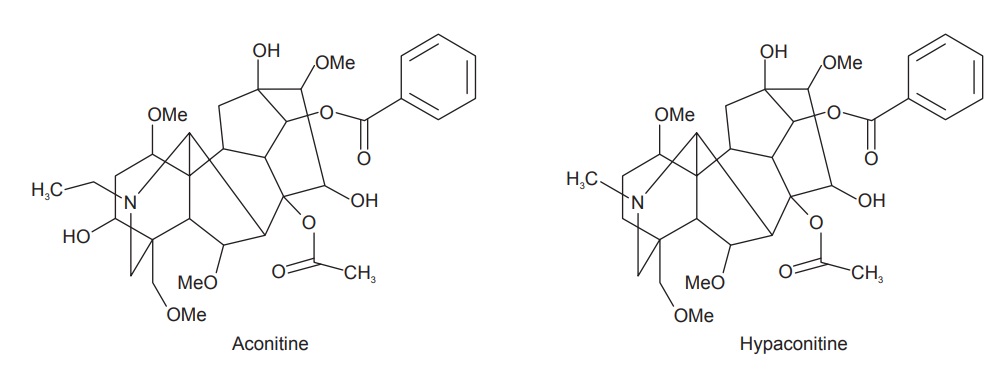
Aconite contains aconitine (0.4–0.8%), hypaconitine,
mesa-conitine, aconine, napelline (isoaconitine, pseudoaconi-tine), neoline,
ephedrine, sparteine, picraconitine, acotinic acid, itaconic acid, succinic
acid, malonic acid, fat, starch, aconosine, 14-acetyineoline, hokbusine A,
senbusines A and C and mesaconitine. The aconitines are diacyl esters of
polyhydric amino alcohols and are extremely poisonous. The basic skeleton of
aconite alkaloid is consisted of a pentacyclic diterpene.
Uses
It is used externally as a local analgesic in liniments and
to treat neuralgia, rheumatism and inflammation. Tincture Aconite is
antipyretic in small doses. Aconitine in amount 2–3 mg can lead respiratory
failure, heart failure and in the end death. The drug is used for the
preparation of an antineuralgic liniment.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparation known as
J.P. Painkill oil (Jamuna Pharma).
